GCP – Enabling next-generation AI workloads: Announcing TPU v5p and AI Hypercomputer
Post Content
Read More for the details.

Post Content
Read More for the details.

We are in the midst of an exciting era of AI-driven innovation and transformation. Today we announced AI Hypercomputer, a groundbreaking architecture that employs an integrated system of AI-optimized hardware, software, and consumption models. With AI Hypercomputer, enterprises everywhere can run on the same cutting-edge infrastructure that is already the backbone of Google’s internal AI/ML research, development, training, and serving.
But the overwhelming demand for TPUs and NVIDIA GPUs makes effective resource management more crucial than ever.
To address this, today we are excited to announce Dynamic Workload Scheduler, a new, simple, and powerful approach to get access to GPUs and TPUs. This blog is for technical audiences to deep-dive into what it is, how it works, and how you can use it today.
Dynamic Workload Scheduler is a resource management and job scheduling platform designed for AI Hypercomputer. Dynamic Workload Scheduler improves your access to AI/ML resources, helps you optimize your spend, and can improve the experience of workloads such as training and fine-tuning jobs, by scheduling all the accelerators needed simultaneously. Dynamic Workload Scheduler supports TPUs and NVIDIA GPUs, and brings scheduling advancements from Google ML fleet to Google Cloud customers. Dynamic Workload Scheduler is also integrated in many of your preferred Google Cloud AI/ML services: Compute Engine Managed Instance Groups, Google Kubernetes Engine, Vertex AI, Batch, and more are planned.
Dynamic Workload Scheduler introduces two modes: Flex Start mode for enhanced obtainability and optimized economics, and Calendar mode for high predictability on job start times.
1. Flex Start mode: Efficient GPU and TPU access with better economics
Flex Start mode is designed for fine-tuning models, experimentation, shorter training jobs, distillation, offline inference, and batch jobs. With Flex Start mode, you can request GPU and TPU capacity as your jobs are ready to run.
With Dynamic Workload Scheduler in Flex Start mode, you submit a GPU capacity request for your AI/ML jobs by indicating how many you need, a duration, and your preferred region. Dynamic Workload Scheduler intelligently persists the request; once the capacity becomes available, it automatically provisions your VMs enabling your workloads to run continuously for the entire duration of the capacity allocation. Dynamic Workload Scheduler supports capacity requests for up to seven days, with no minimum duration requirement. You can request capacity for as little as a few minutes or hours; typically, the scheduler can fulfill shorter requests more quickly than longer ones.
If your training job finishes early, you can simply terminate the VMs to free up the resources and only pay for what your workload actually consumed. You no longer need to hold onto idle resources just to use them later.
If you’re using GKE node pools for your AI/ML workloads, an easy way to use Dynamic Workload Scheduler is through orchestrators such as Kueue. Popular ML frameworks such as Ray, Kubeflow, Flux, PyTorch and other training operators are supported out of the box. Here are the steps to enable this:
Step 1: Create a node pool with the “enable-queued-provisioning” option enabled.
Step 2: When you create your GKE job, label it to indicate that Kueue and Dynamic Workload Scheduler should run it. Kueue does the rest: it will automatically do a capacity request and handle the job start orchestration.
2. Calendar mode: Reserved start times for your AI workloads [Preview Q1’ 24]
Calendar mode caters to training and experimentation workloads that demand precise start times and have a defined duration. This mode extends the future reservation capabilities announced back in September.
With Calendar mode, you will be able to request GPU capacity in fixed duration capacity blocks. It will initially support future reservations with durations of 7 or 14 days and can be purchased up to 8 weeks in advance. Your reservation will get confirmed, based on availability, and the capacity will be delivered to your project on your requested start date. Your VMs will be able to target this reservation to consume this capacity block. At the end of the defined duration, the VMs will be terminated, and the reservations will get deleted.
Step 1: Create a calendar mode future reservation.
Step 2: Run VMs with the specific reservation affinity and specify the reservation delivered at the desired start date via Compute Engine, Managed Instance Groups, or GKE APIs as available today.
Dynamic Workload Scheduler is built on Google Borg technology, which is responsible for real-time scheduling of millions of jobs on the Google ML Fleet, including one of the largest distributed LLM training jobs in the world (as of November 2023). With Flex Start and Calendar modes, Dynamic Workload Scheduler can provide you with more flexibility, improved access to GPUs and TPUs, better resource utilization, and lower costs. Customers and partners are already seeing the benefits of Dynamic Workload Scheduler.
Here is what Linum AI, a text-to-video generative AI company, had to say:
“The new Dynamic Workload Scheduler scheduling capabilities have been a game-changer in procuring sufficient GPU capacity for our training runs. We didn’t have to worry about wasting money on idle GPUs while refreshing the page hoping for sufficient compute resources to become available.” – Sahil Chopra, Co-Founder & CEO, Linum AI
sudoAI, a 3D generative AI company, trained its latest generative model using APIs enabled by Dynamic Workload Scheduler.
“We really like the convenience of finding capacity each time we need it without needing to worry about it. It enabled us to test new ideas, iterate, and also run longer training runs. We were able to fully train our latest 3D Gen AI model using the new Dynamic Workload Scheduler functionality and meet our internal deadlines to launch.” – Robin Han, Co-Founder and CEO, sudoAI
Get started today with Dynamic Workload Scheduler-enabled APIs. Learn how to deploy GPUs using the Google Kubernetes Engine ProvisioningRequest API and Kueue. For TPUs, you can use Kubernetes Engine or directly through Queued Resources.
Read More for the details.

The automotive industry stands at the precipice of a profound transformation, spurred by the imperatives of sustainability utilizing technology and climate innovation. Amidst increasing climate concerns, regulatory pressures, and the demands of consumers and investors alike, automakers and their suppliers are actively steering towards a more sustainable horizon and taking accountability.
The conversation around sustainability has shifted from a peripheral concern to a central strategy for business growth and resilience. Despite a plethora of public commitments to sustainability, only a fraction of companies are actively executing relevant programs and measuring outcomes against set targets. This gap underscores a broader challenge: the need for precise and verifiable sustainability metrics and tools that are able to measure results and progress. Here, the vital role of technology innovation, particularly AI, in realizing the sustainable transformation cannot be overstated.
1. AI-enabled sustainable supply chains
Resilient supply chains are synonymous with sustainable ones as they can adapt better to changing circumstances and minimize the impact of disruptions. The automotive industry, facing an era marked by unprecedented disruptions, from pandemics to climate-induced events, is turning to AI to build solutions that help companies to connect and monitor their whole supply chain ecosystems. Technologies such as Prewave’s real-time social media and news media monitoring tool, or NGIS/TraceMark real-time sustainable sourcing monitoring platform, are instrumental in crafting supply chains that adhere to environmental, social, and governance standards, for instance utilized by Unilever.
2. Advancements in manufacturing
The Renault Group illustrates how AI analytics can lead to more energy-efficient manufacturing processes. The integration of AI in monitoring and optimizing energy consumption demonstrates substantial reductions of 25% in energy consumption, aiming to reduce an additional 25% by 2025, a precedent for the industry. Such initiatives exemplify the role of AI in operationalizing energy conservation and realizing sustainability objectives.
3. The AI-driven evolution of car design
The collaboration between Volkswagen and Google Cloud epitomizes the transformative impact of AI in vehicle design. By harnessing machine learning algorithms, Volkswagen has significantly expedited the car design process, compared to traditional, resource-intensive aerodynamic testing methods like wind tunnel testing. This not only underscores the cost-effectiveness of AI but also its potential to accelerate more sustainable development of environmentally optimized vehicles.
4. Intelligent charging as enabler for the green energy transition
The advent of bi-directional charging in electric vehicles (EVs) is a significant milestone towards a greener automotive future, enabling not only power supply to homes during outages but also the stabilization of the electric grid. Intelligent charging, empowered by AI, offers enhanced prediction and management of the battery cycle life, promoting efficient energy use. Another example of AI-led innovation is Renault’s peer-to-peer charging service, easing the adoption of EVs by improving access to charging infrastructure and fostering a community-based approach to energy management. This smart integration of technology is pivotal in driving the green energy transition in the automotive industry.
5. The future of mobility in the AI era
The advancement of autonomous vehicles is another frontier where AI is proving indispensable. Cruise’s application of Google Cloud’s AI enhances the software development for autonomous vehicles, i.e., optimizing safety and operational efficiency. Furthermore, Google Maps’ AI features are redefining mobility by recommending eco-friendly routes and improving the accessibility of EV charging infrastructure.
As we delve deeper into the capabilities of AI, its potential to drive sustainability in the automotive sector becomes increasingly evident. As leaders and decision-makers in this space, it’s incumbent upon us to harness the capabilities of AI not as a mere adjunct but as a central driver of sustainable innovation. The convergence of AI with our industry’s complex ecosystem presents a unique chance to simultaneously redefine operational excellence and environmental stewardship.
Google Cloud stands ready to partner with pioneers committed to integrating AI into their strategic roadmap. By joining forces, we can catalyze a significant shift, employing AI to fortify supply chains, refine manufacturing workflows, and craft the coming generation of vehicles with sustainability embedded at their outset. Now is the time to decisively embark on this transformative venture, to synergize, pioneer, and navigate the journey towards a sustainable trajectory in the automotive industry.
We’ll be blogging throughout COP28; follow along here.
Read More for the details.
Success is often measured by one’s ability to harness and interpret data effectively. The journey begins with centralizing and analyzing marketing data in real time, a game-changing approach that can drive impactful decisions and elevate campaign strategies.
In this blog post, we’ll explore how Google Cloud and Fivetran, a SaaS data integration platform, can help you centralize and analyze your marketing data in real time. Fivetran can take care of multiple steps in the ELT and automated data ingestion journey. We’ll share real-world examples of how organizations are using real-time analytics to improve their results, and we’ll discuss the benefits of this approach for businesses of all sizes.
A large healthcare organization recognized the transformative power of data and analytics, and embarked on a mission to harness their expertise and insights to fuel exponential growth and success. Their challenge was despite their successful marketing strategies that increased demand generation, concerns arose due to rising budgetary expenses and reductions in campaign spending. The marketing team encountered difficulties in accurately measuring campaign performance and efficiency, identifying the specific initiatives responsible for marketing outcomes, and procuring timely insights from their agency for informed decision-making.
The marketing team recognized that the challenge was with the data scattered across various applications, databases, and file systems. This fragmentation and lack of centralization of marketing data hindered their ability to analyze and optimize campaign performance, track and optimize spending across different channels, and accurately measure healthcare enrollment attribution and conversion rates. Consequently, optimizing advertising expenditures and acquiring holistic performance metrics remained unattainable.
The lack of a centralized data repository became acutely apparent when they were asked a question: ‘What’s working well?’ Their response, ‘nothing,’ underscored the critical need for a unified data strategy. This realization marked a turning point, igniting a journey towards data-driven marketing excellence.”
The team’s aspiration was clear to create a data-driven decision-making process that would seamlessly integrate with their datasets and deliver measurable benefits. Key considerations to maximize data value included data usage patterns, data sources from both external and internal sources, primary workloads, data platforms, and enrichment and transformation requirements.
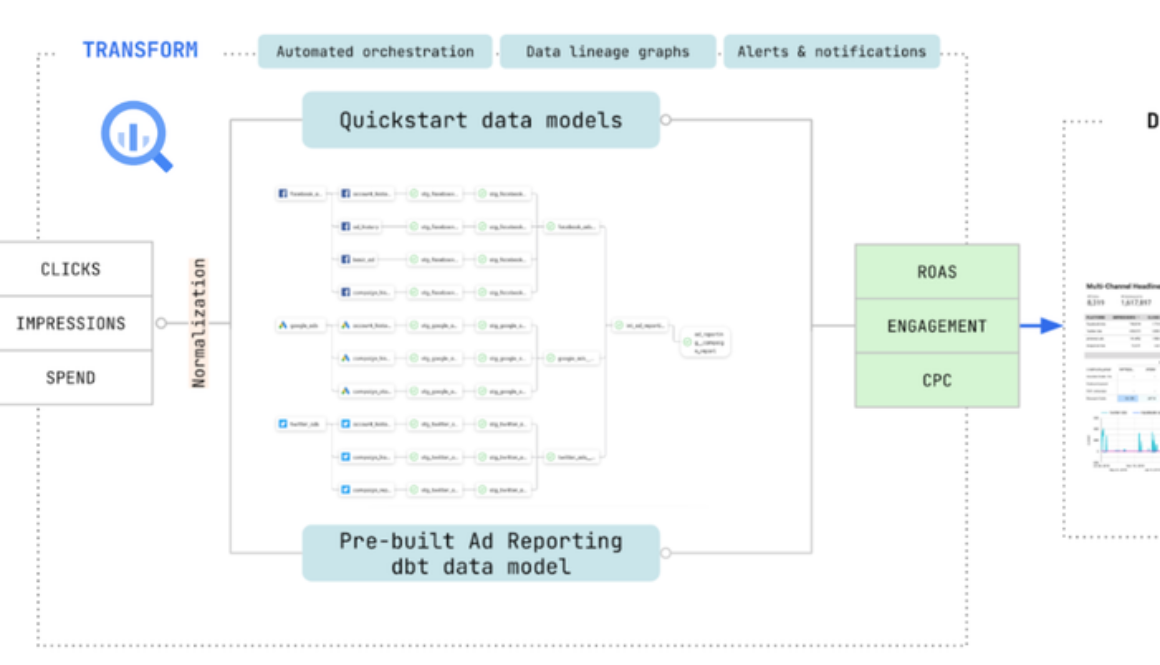
To resolve their data quandary, this forward-thinking company turned to Google Cloud and Fivetran, whose partnership provided a swift and effective means to eliminate data silos and centralize their marketing data. This harmonious integration unlocked a wealth of possibilities, depicted in the diagram below:
Fivetran’s automated data movement platform supports a wide range of marketing analytics data sources with out-of-the-box, no-code, self-serve connectors. These connectors include social media and ad platforms, email, marketing analytics platforms, CRM solutions, and various databases and object stores.
The integration with Google BigQuery and other Google Ads services seamlessly provided end-to-end automation and reliability, complete with customizable sync schedules, normalized schemas for organized and understandable data, and even pre-built data models tailored for marketing data sources. This approach empowers the marketing team to swiftly act on crucial metrics like click-through rates, ad spend efficiency, and more while enhancing performance and efficiency.
Centralizing their data enhances efficiency, allowing the team to prioritize strategic planning, campaign optimization, and improving customer engagement. By making data accessible and organized, the CMO and the marketing team can focus on delivering even better service and engagement to their audience.
If you’d like to dig deeper into how Fivetran and Google Cloud are working together to enhance marketing analytics, check out our “Unlocking the Power of Marketing Analytics with Fivetran and Google Cloud” on-demand hands-on lab.
When faced with the challenge of “real-time analytics,” the initial response often triggers a fundamental question: What exactly defines “real-time”? Does it mean millisecond-level latency, subsecond response times, seconds, minutes, hours, or even daily updates? The answers can vary widely based on the specific use case and the perspective of those asked.
Traditionally, analytics platforms don’t dive into millisecond-level operational surveillance of individual events or sensor data — that’s the realm of highly specialized hardware and software designed for specific physical domains where data is generated, typically found in operational technology environments.
When discussing common analytics workloads like cloud data warehousing, data lakes, data applications, data engineering, AI/ML, and more, the term “real-time” can be somewhat misleading. Instead, a more precise description for what Google Cloud and Fivetran offer in analytics workloads is “continuous” data processing, aligning more closely with the reality of data flow and insights.
By focusing on specific use cases and desired outcomes, the importance of continuous data movement at intervals ranging from one minute to 24 hours becomes evident. It’s crucial to align this requirement with business justification, weighing the cost and effort against the value and necessity.
Frequently, scenarios arise where continuous replication and change data capture are essential, especially when dealing with significant incremental changes to data sources, often measuring in tens or hundreds of gigabytes per hour.
For example, let’s consider the case of a typical SAP ERP customer, such as a global logistics company. They operate a substantial SAP S/4HANA environment, generating a significant volume of transactions, resulting in high change data volumes exceeding 100 gigabytes per hour due to updates, inserts, and deletes. Fivetran continuously replicates this S/4HANA data to Google Cloud BigQuery, integrating it with other datasets Fivetran ingests, including operational databases and their enterprise customer management system. The aim is to provide a comprehensive global view of supply chain effectiveness and operational efficiency, supporting continuous decision-making throughout the day.
The term “real-time” can vary among organizations and use cases. However, in the realm of analytics, continuous data movement proves to be a reliable method for attaining desired results. Leveraging Fivetran to consistently replicate SAP data into Google Cloud BigQuery enables organizations to gain a comprehensive perspective of their operations and make faster, more insightful decisions.
Our customers are transforming their businesses by integrating their applications with Google Cloud and Fivetran offerings, such as Oakbrook Financial. Our goal is to make this journey easier for our customers and help them to grow their data analytics business on Google cloud. With Google Cloud’s holistic cloud migration and modernization program, Google Cloud RaMP, you can easily gain insight into your current landscape and estimate the total cost of migration. You can learn more about how Google Cloud can help accelerate your data modernization journey, visit our page here. To know more about using Fivetran to unlock business intelligence in BigQuery. review the documentation available here or visit the Fivetran resources page.
Read More for the details.
Businesses are under increased pressure to do more with less, while customer expectations and demands have never been higher. Today’s enterprises need a way to be more productive, effective, and responsive while still addressing the operational challenges of cost containment, risk reduction, security, and compliance.
Google Cloud partner of 15 years, EPAM Systems, a leading digital transformation services and product engineering company, aims to address these challenges with Vivien, a digital metahuman that the company introduced at Google Cloud Next ’23.
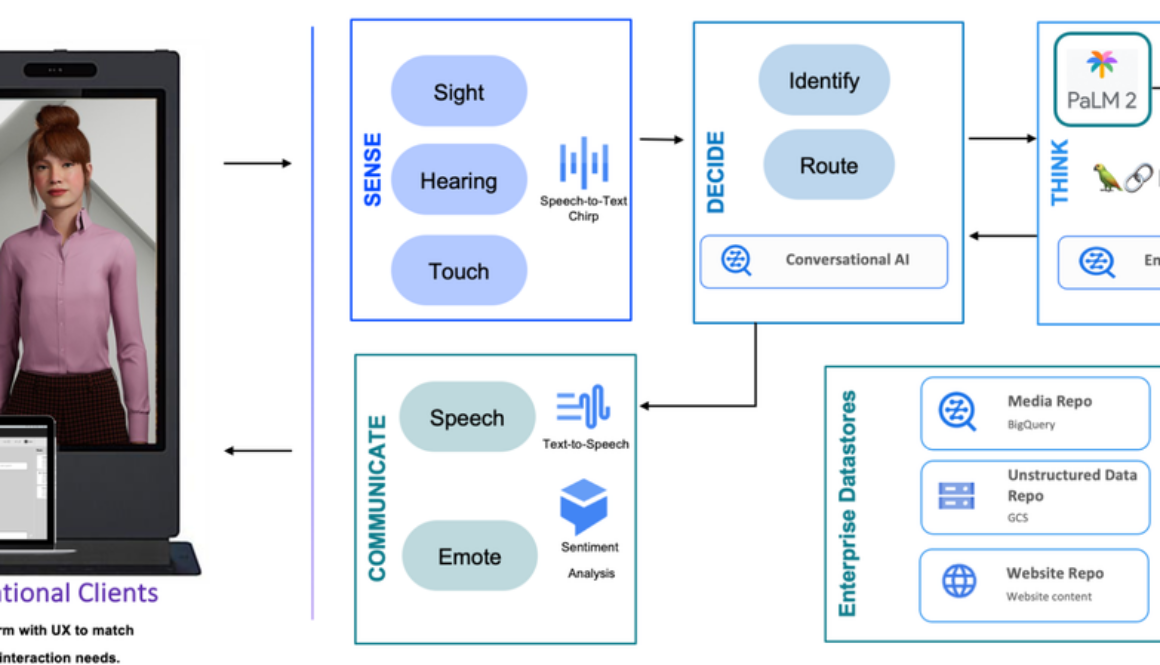
Using the power of generative AI, Vivien, a state-of-the-art Digital Human, is built on the powerful combination of Unreal Engine and Vertex AI. Vivian is an end-to-end, secure, and scalable solution that can be configured to any industry or business vertical. Vivien’s appearance and voice can also be customized to portray the customer’s desired image.
Vivien is a modular product, backed by a SaaS solution that customers can deploy within their existing Google Cloud environment in their dedicated tenant. Vivien’s capabilities as a digital assistant allow for interaction with customers in a variety of ways including voice and text. Vivien can be further configured to have a specific personality, to search and summarize structured and unstructured data, and has the ability to integrate with Looker to provide visual analytics and actionable insights.
Vivien’s capabilities are designed to address a wide range of customer challenges related to efficiency, task management, personalization, and decision-making. Benefits include:
Personalization: Ability to learn user preferences leads to tailored recommendations and responses, ensuring that users receive the most relevant and helpful information possible.Integration: Vivien is integrated with Vertex AI, providing a reliable and robust digital assistant experience that is scalable and secure.Insightful analysis: Data-driven insights help users make informed decisions. By leveraging Vivien’s analytical capabilities, users can gain deeper understanding from complex datasets.
Examples of Vivien’s benefits across specific industries include:
Healthcare: Contribute to patient care by utilizing data-driven insights to enhance safety and efficacy.Finance: Enhance investment strategies and risk management with Vivien’s predictive analytics.Retail: Build promotion strategies, analyze marketing campaigns, onboard new employees, and create shopper experience assistant solutions to increase loyalty.
Incorporating Vivien into a customer’s ecosystem offers advantages, from tailored personalization to tight integration and insightful analysis. Offerings include:
Natural conversations: Engage in seamless, human-like dialogues with Vivien. Her advanced Natural Language Processing (NLP) skills ensure effortless interactions.Simplified task management: Easily assign tasks to Vivien. Whether it’s scheduling appointments or retrieving data, it serves as your virtual assistant in streamlining daily operations.In-depth data analysis: Leveraging Vivien’s data analysis capabilities, gain valuable insights from complex datasets for making well-informed decisions.
Vertex AI Conversation is a key component of Vivien, which provides the conversational engine that powers the platform’s many features. Vertex AI Conversation provides a single powerful platform for building conversational AI solutions that use Generative AI on Vertex AI. This combination of technologies allows the creation of virtual agents that can understand and respond to natural language in a human-like way, even for complex or difficult requests.
Enterprise search capabilities based on corporate structured and unstructured data
Vivien is a multi-domain chatbot that can be configured to meet the needs of any business. Customers can configure Vivien’s personality, tone, and language to match their brand. They can also provide Vivien with access to data from their Cloud Storage environment, BigQuery, Jira, and intranet data so that Vivien can answer questions, provide summarization, and links to the resources used for the responses.
Sentiment analysis, responsible AI Integration, masking language corpus
Using Unreal Engine and custom natural language processing (NLP) sentiment analysis, Vivien achieves a lifelike representation that pushes the boundaries of digital personas. The appearance is highly authentic, blurring the line between virtual and reality.
While generative AI has the potential to revolutionize the customer experience, there are also a number of challenges worthy of addressing.
When using generative AI, a key concern is reliability. To ensure trustworthy and accurate results from large language models (LLMs), Vivien applies constraints and guardrails. These measures ensure that the results are grounded in reliable evidence and logically sound explanations. Vivien’s approach prevents the generation of answers without grounding them in human-approved domain models or credible evidence, thus reducing the risk of hallucinations.
Businesses looking to embrace the potential of generative AI should begin by educating themselves about the technology and experimenting with its applications to enhance the customer experience. Finally, it’s crucial for businesses to prioritize the development of policies and procedures for the responsible use of generative AI.
Vivien’s solution, powered by Google Cloud Generative AI on Vertex AI, addresses industry-specific challenges, and enhances outcomes. In healthcare, Vivien elevates patient care, optimizes investment strategies in finance, and boosts customer loyalty in retail. Vivien delivers efficient, personalized, and data-driven results.
EPAM and Google Cloud’s 15-year partnership blends innovative technology and services. By leveraging our combined strengths in large language models, cloud-based solutions, and AI technology, we are driving innovation and delivering transformative solutions to our customers. This collaboration aligns perfectly with EPAM’s core values and innovation strategy, enabling us to push the boundaries of technology and make a real impact on our customers’ businesses.
Partnering with Google Cloud allows EPAM to leverage their expertise with LLMs and cloud-based solutions while focusing on their unique AI technology for deep content understanding and sophisticated logical reasoning.
Learn more about Google Cloud’s open and innovative generative AI partner ecosystem. Read more about the partnership between EPAM and Google Cloud here and request additional information here.
Read More for the details.
Editor’s note: Headquartered in Barcelona, eDreams ODIGEO (or eDO for short) is one of the biggest online travel companies in the world, serving more than 20 million customers in 44 countries. Read on to learn about how they modernized their legacy data warehouse environment to a data mesh built on BigQuery.
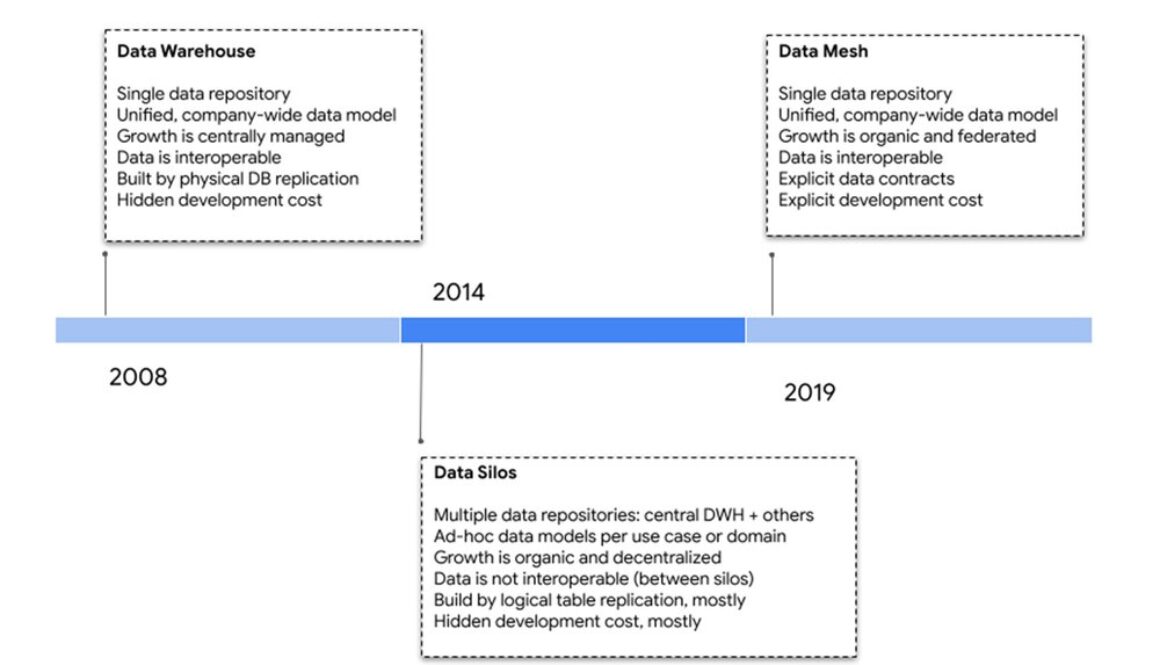
Data analytics has always been an essential part of eDO’s culture. To cope with exponential business growth and the shift to a customer-centered approach, eDO evolved its data architecture significantly over the years, transitioning from a centralized data warehouse to a modern data mesh architecture powered by BigQuery. In this blog, a companion to a technical customer case study, we will cover key insights from eDO’s data mesh journey.
Initially, eDO had a centralized data team that managed a data warehouse. Data was readily available and trusted. However, as the company grew, adding new data and adapting to increasing complexity became a bottleneck. Some analytics teams built their own pipelines and silos, which improved data availability and team autonomy but introduced challenges with data trust, quality, and ownership.
As teams and complexity grew, data silos became intolerable. AI and data science needs only made the need for a unified data model more pressing. In 2019, building a centralized model with a data lake would have been the natural next step, but it would have been at odds with the distributed e-commerce platform, which is organized around business domains and autonomous teams — not to mention the pressure of data changes imposed by its very high development velocity.
Instead, eDO embraced the data mesh paradigm, deploying a business-agnostic data team and a distributed data architecture aligned with the platform and teams. The data team no longer “owns” data, but instead focuses on building self-service components for producers and consumers.
The eDO data mesh and data products architecture
In the end, eDO implemented a business-agnostic data platform that operates in self-service mode. This approach isolates development teams from data infrastructure concerns, as is the case with a traditional centralized data team. It also isolates the data platform team from any business knowledge, unlike a traditional centralized data team. This prevents the data team from becoming overloaded by the ever-increasing functional complexity of the system.
The biggest challenges for adopting data mesh are cultural, organizational, and ownership-related. However, engineering challenges are also significant. Data mesh systems must be able to handle large volumes of data, link and join datasets from different business domains efficiently, manage multiple versions of datasets, and ensure that documentation is available and trustworthy. Additionally, these systems must minimize maintenance costs and scale independently of the number of teams and domains using them.
To build its data mesh, eDO chose a number of Google Cloud products, with BigQuery at the heart of the architecture. These technologies were chosen for their serverless nature, support for standard protocols, and ease of integration with the existing e-commerce platform.
One key enabler of this architecture is the deployment of data contracts. These contracts are:
Owned exclusively by a single microservice and its teamImplemented declaratively using Avro and YAML filesDocumented in the Avro schemaManaged in the source code repository of the owning microservice
Declarative contracts enable the automation of data ingestion and quality checks without requiring knowledge of business domains. Exclusive ownership of contracts by microservices and human-readable documentation in a git repository help producers take ownership of their contracts.
Finally, when it comes to data architecture, the platform has four types of data products: domain events, snapshots, derivatives and quality records that fulfill different access patterns and needs.
eDO learned a lot during the four years since the project started and have many improvements and new features planned for the near future.
Lessons learned:
Hand-pick consumer stakeholders who are willing and fit to be early adopters.Make onboarding optional.Foster feedback loops with data producers.Data quality is variable and should be agreed upon between producers and consumers, rather than by a central team.Plan for iterative creation of data products, driven by real consumption.Data backlogs are part of teams’ product backlogs.Include modeling of data contracts in your federated governance, as it is the hardest and riskiest part.Consider Data Mesh adoption a difficult, challenging engineering project, in domain and platform teams.Documentation should be embedded into data contracts, and tailored to readers who are knowledgeable about the domain of the contract.
Work on improving the data mesh continues! Some of the areas include:
Improved data-quality SLAs – working on ways to measure data accuracy and consistency, which will enable better SLAs between data consumers and producers.Self-motivated decommissions – experimenting with a new “Data Maturity Assessment” framework to encourage analytical teams to migrate their data silos to the data mesh.Third-party-aligned data contracts – creating different pipelines or types of data contracts for data that comes from third-party providers.Faster data timeliness – working on reducing the latency of getting data from the streaming platform to BigQuery.Multi-layered documentation – deploying additional levels of documentation to document not only data contracts, but also concepts and processes of business domains.
Data mesh is a promising fresh approach to data management that can help organizations overcome the challenges of traditional centralized data architectures. By following the lessons learned from eDO’s experience, we hope organizations can successfully implement their own Data Mesh initiatives.
Want to learn more about deploying Data Mesh in Google Cloud? See this technical white paper today.
Read More for the details.
Trino is a popular, open-source, distributed SQL query engine for data lakes and warehouses. It is used by many businesses to analyze large datasets stored in Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), Cloud Storage, and other data sources. Dataproc is a managed Hadoop and Spark service that makes it easy to set up and manage clusters. However, Dataproc currently does not support autoscaling for workloads that aren’t based on Yet Another Resource Negotiator, or YARN, such as Trino.
Autoscaling Dataproc for Trino addresses the lack of autoscaling support for non-YARN based workloads, preventing overprovisioning, underprovisioning, and manual scaling efforts. It automatically scales clusters based on workload demand, saving cloud costs, improving query performance, and reducing operational workload. This makes Dataproc a more attractive platform for Trino workloads, enabling real-time analytics, risk analysis, fraud detection, etc. In this blog post, we present a solution that provides autoscaling for Trino when running on a Dataproc cluster.
Hadoop is an open-source software framework for distributed storage and processing of large datasets across a cluster of computers. It provides a reliable, scalable, and distributed computing platform for big data processing. Hadoop utilizes a YARN centralized resource manager to allocate resources, monitor, and manage the cluster.
Trino can use various data sources like Hadoop, Hive, and other data lakes and warehouses, allowing users to query data in different formats and from different sources using a single SQL interface.
In Trino, resource allocation and management are driven by the Trino Coordinator, which is responsible for query coordination, planning, and resource allocation. Trino dynamically allocates resources (CPU and memory) on a fine-grained level for each query. Trino clusters often rely on external cluster management systems like Kubernetes for resource allocation and scaling. These systems handle cluster resource provisioning and scaling dynamically. Trino does not use YARN for resource allocation when running on Hadoop clusters.
Dataproc is a managed Hadoop and Spark service, providing a fully managed environment for big data workloads on Google Cloud. Dataproc currently only supports autoscaling for YARN-based applications. This poses a challenge for optimizing the costs of running Trino on Dataproc, as the cluster size should be adjusted based on current processing needs.
Autoscaler for Trino on Dataproc solution provides reliable autoscaling for Trino on Dataproc without compromising workload execution.
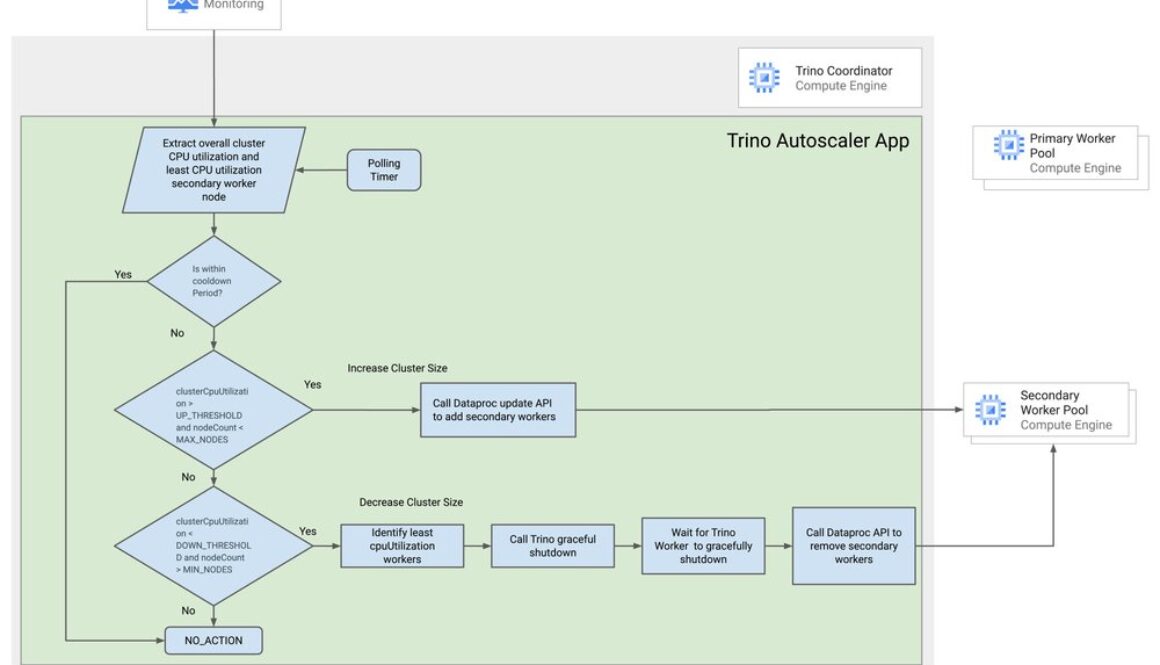
Trino deployment on Dataproc uses Trino’s embedded discovery service. Every Trino node connects with the discovery service on startup and periodically sends a heartbeat signal.
When adding an extra worker to the cluster, the worker registers with the discovery service, allowing the Trino coordinator to start scheduling new tasks for the new workers. But removing a worker from the cluster can be difficult if a worker suddenly shuts down, which can result in complete query failure.
Trino has a graceful shutdown API that can be used exclusively on workers in order to ensure they terminate without affecting running queries. The shutdown API puts the worker in a SHUTTING_DOWN state and the coordinator stops sending new tasks to the workers. In this state, the worker will continue to execute any currently running tasks, but it will not accept any new tasks. Once all of the running tasks have finished executing, the Trino worker will exit.
This Trino worker behavior requires the Trino Autoscaler solution to monitor workers to ensure that they gracefully exit before removing the VMs from the cluster.
By polling the Cloud Monitoring API, the solution monitors the cluster’s CPU utilization and the details of the least CPU-utilized secondary worker nodes. After each scaling action, there is a cooldown period during which no other scaling action is taken. The cluster is scaled up or down based on CPU utilization and worker node count.
Cluster sizing decisions are made based on overall CPU utilization, and the node to be removed is based on the secondary worker node using the least CPU.Increasing or decreasing cluster size only adds or removes secondary worker nodes, which are preemptive VMs by default, and avoids any interruption to HDFS workloads.The application runs on the coordinator node, and autoscaling is disabled by default in Dataproc.The addition of new workers will only help new job submissions; existing jobs continue to run on bound workers.
The above graphs show the results of running the solution, indicating the increase or decrease in the number of workers based on whether the average CPU utilization is increasing or decreasing. The solution clearly labels the workers in the process of shutting down.
Automatic scaling of your Dataproc cluster based on workload can ensure that you only use the resources you need. Autoscaling can lead to significant cost savings, especially for workloads that experience variable demand.
In addition to optimizing cost, the autoscaling solution can help improve performance by scaling up your cluster during times of high demand, ensuring that your queries are processed quickly and efficiently. This can come in handy for time-sensitive workloads, such as real-time analytics.
To get started, follow our step-by-step guide.
Read More for the details.

At COP28, accelerating the scale and deployment of finance across sectors continues to be a high priority to drive climate action. In the COP28 President’s letter to all parties, Dr. Sultan Ahmed Al Jaber stated that “Finance is a critical enabler of climate change.” The good news is the financial services sector is stepping up in its role to accelerate industry decarbonisation and find innovative financing solutions for issues like climate risk, water & food stress and nature loss.
Companies like HSBC and ING have made massive commitments toward providing access to sustainable financing and investments over the past few years, including HSBC’s commitment of $750 million to $1 trillion by 2030 and most recently $600 million from ING and the European Investment Bank to help fund climate transition initiatives.
Working with customers in Europe, Middle East and Africa, we are keenly aware of this impact challenge and how Google Cloud can help to solve for climate change with technology. Specifically, we’ve focused on how AI and data can help companies unlock the capabilities they need to meet their climate commitments.
Recently, our AI capabilities have exploded with the rise of generative AI and large language models (LLMs), putting enhanced powers of data aggregation and analysis into our customers’ hands. Using natural language to ask questions of your data will become the new normal, and we expect that this will be key to unlocking new innovations in the future. Two stories from European banking customers help illustrate this.
The first is HSBC. Noel Quinn, CEO has said they are “committed to the transition to net zero.” HSBC has long been innovating using Google Cloud technology for their customers. One example is HSBC’s risk advisory solution built on Google Cloud. This project helps their fixed-income traders improve their what-if simulations and their ability to service their customers in the context of climate impact. HSBC uses this technology as a reflection of their philosophy that sustainability and climate risk are no longer isolated categories within a business. Rather, they are a part of every person’s job.
Similarly, ING has built a solution that generates early warning signals related to client behavior for their wholesale banking portfolio managers in near real-time, based on external data, (e.g. world-wide news, climate risk, ESG impact, human rights abuses, bankruptcy, fraud, etc). What is compelling about this solution is the sheer volume of data that is processed daily for these portfolio managers using AI. Climate impact cuts across all aspects of company operations, and this solution helps ING’s commercial banking division surface relevant insights to act upon.
Companies must urgently respond to the climate agenda – both to decarbonise but also act on the climate risks to their business. AI and cloud technologies will be critical in bringing business insights for targeted action and unlocking new sources of value.
To learn more about how we help companies solve their sustainability challenges using data and AI, in the finance sector and others, please visit our site, or connect with us on LinkedIn.
We’ll be blogging throughout COP28; follow along here.
Read More for the details.

As the effects of climate change play out before our eyes, the need for climate action has never been more urgent. It’s not just the global public advocating for change. With climate-related disasters costing the world economy more than $500 billion a year, business leaders are also focused on taking climate action. CEOs rank sustainability a top priority, 37% more frequently in 2022 than in the previous year.
Google has set an ambitious goal to reach net-zero emissions across our operations and value chain by 2030, and we’re committed to working with our customers and partners to develop new sustainability solutions and help apply technology like artificial intelligence (AI) to support climate efforts.
For example, we launched the Google Cloud Ready Sustainability program last year to help customers identify and deploy sustainability solutions developed by our ecosystem of partners. The program spotlights partner solutions built on Google Cloud and that leverage specific climate and ESG-related domain expertise alongside capabilities in AI and earth observation from Google Cloud. These solutions are supporting customers across important areas like digital sustainability, ESG performance management, sustainable sourcing, fleet electrification, energy optimization, and green financing.
Google Cloud Ready Sustainability partner ESG Book gives financial markets access to the information to understand companies’ sustainability practices, enabling investors to make informed investment decisions.
ESG Book is utilizing Google Cloud AI to help customers make sense of this vast volume of data. For instance, Google Cloud Document AI automates components of the workflow of searching for documents containing relevant ESG information, parsing those documents for pertinent data, then extracting that data and using it to populate structured datasets that can be sold to investors to inform their investment decisions. Using AI to automate its workflow in this way, ESG Book believes it is possible to improve efficiency on manual data collection efforts by around 50%, freeing its team to develop more products to help decarbonize the economy.
One such product is its news sentiment analysis tool, which uses AI to collate, summarize, and analyze the sentiment of millions of news articles to gain insights into companies’ sustainability and environmental practices beyond those covered by the businesses’ own reporting. By converting this sentiment into a score, ESG Book’s AI workflow helps create an augmented rating for each company, providing an outside-in view, enabling financial markets to invest in the most sustainable businesses.
Watershed, another Google Cloud Ready Sustainability partner, is an enterprise climate platform that helps businesses reduce their emissions and remove millions of tons of carbon from the atmosphere. With Google Cloud, Watershed is able to work at scale to bring granular, auditable sustainability reporting into businesses’ everyday decision making, enabling emissions-reduction programs such as decarbonizing supply chains to build products with a low-carbon footprint, like Everlane’s sneakers.
In order to provide this level of detail on supply-chain emissions, Watershed’s models depend on the most up-to-date data for every part of the process. If you put in an outdated figure for the energy needed to manufacture a certain sweater, for example, the modeled figure for the entire supply chain could be distorted. So Watershed is experimenting with using AI to measure, collect, and update data more frequently, as well as synthesizing the data to look for trends and patterns to inform its modeling, ensuring its emissions reporting is as accurate as possible.
Both Watershed and ESG Book are especially excited about the potential of generative AI (gen AI) not only to further streamline their processes, but to offer new products and services that will transform the ways customers interact with their carbon emissions data. Watershed’s vision of gen AI is to help transform a vast amount of unstructured, text-based data in corporations’ supply chains into a format that can be used in its modeling, improving the efficiency of its internal processes. Meanwhile, offering customers the ability to use large language models (LLMs), trained on relevant sustainability datasets, to write their ESG reports would save businesses significant amounts of time, which they could use to focus on working towards sustainability targets.
ESG Book already uses AI to estimate corporate GHG emissions, but is exploring how it could use gen AI to enable investors such as asset managers and investment banks to interrogate its vast datasets in entirely new ways. Right now, the screening and visualization tools ESG Book offers are highly structured. But with gen AI, ESG Book plans to enable customers to use unstructured, natural language questions to mine its data in unlimited ways, unearthing insights such as trend analysis, heatmaps, correlations, or highly specific requests that are currently difficult to scale. ESG Book hopes to empower its clients to use its data to get unprecedented insights into companies’ sustainability practices, enabling an even more targeted flow of investment to companies preparing for a decarbonized future.
The use of AI in helping businesses operate more sustainably is still in its early stages, but as the experience of Watershed and ESG Book already shows, the potential is great for partner-driven AI solutions to transform the ways businesses think about and act on environmental sustainability. With both environmental and economic pressures, AI has an important role to play in helping drive a carbon-free future. Given the scale of the challenge we face, that is something worth getting excited about.
We’re blogging throughout COP28; follow along here.
Read More for the details.

Camanchaca, a Chilean seafood exporter with a rich 58-year heritage, is renowned for its commitment to sustainable sourcing and exporting of salmon, jack mackerel, and shellfish. With a workforce of 3,800 employees, Camanchaca continuously cultivates a culture of innovation that touches every aspect of its business. This forward-thinking philosophy led to the recognition of the transformative potential of generative AI technologies for its operations.
Five years ago, a strategic decision was made to migrate enterprise workloads to Google Cloud, and to leverage the power of BigQuery, Looker, and Cortex Framework. This foundational digital architecture enabled Camanchaca to unleash the power of its vast enterprise data with the introduction of Elon, a groundbreaking generative AI agent designed for the enterprise.
Elon revolutionizes the way employees interact with core enterprise data. With secure data access systems, the generative agent has democratized data access, making it available to every employee, regardless of technical expertise. This has empowered users to reach Camanchaca’s rich structured and unstructured data, enabling them to make informed decisions by simply asking a question. In response, Elon delivers a personalized, meaningful and concise answer. For example, when asked about the number of purchase orders or the volume of a particular SKU in the warehouse, Elon seamlessly combines information from different datasets to provide a cohesive, single-sentence response.
This modern data interaction enhances decision-making abilities without the time-consuming task of manually sifting through and assembling data. Picture the Financial Controller, once clicking through dashboards and application screens to gather purchase order and procurement information, now served with accurate and contextual insights in natural-language response.
“Creating Elon with the power of Google Cloud’s Generative AI has been a huge step in our technological innovation journey,” said Andrés Mora, Business Intelligence Lead, Camanchaca.
In eight weeks, Camanchaca developed Elon by leveraging Google Cloud’s PaLM 2 for Text model to extract information from a text file (CSV) containing production data. A web-based user interface was developed to connect the Vertex AI API the text files to the training models, and then an interface was built to be user-friendly for employees accessing Elon while on the go. The interface connects the enterprise data from BigQuery to the large language model, resulting in natural language responses following automatic response patterns. Camanchaca’s corporate devices bring Elon to life with voice-enabled commands replacing the process of manual data search with hands-free voice prompts.
This paradigm shift is bringing remarkable change at Camanchaca. Andrés Mora, Business Intelligence Lead, highlights the transformation mindset that pervades Camanchaca: “Leaders expect and demand innovation and invention from their teams and are always seeking ways to simplify. They remain informed of what’s going on around them, look for new ideas everywhere, and are not limited by a ‘we didn’t invent it here’ mindset.”
Camanchaca shares that this journey with generative AI innovations is just beginning, and the possibilities for transforming business operations, interacting with data, and serving their customers are endless. Looking ahead, Camanchaca plans to extend generative agent access to its suppliers and vendors, explore AI for predictive maintenance, and begin blending first party data with public data for increased insights with Google Cloud.
Read More for the details.

In retail, the distinction between physical and digital has blurred, and the home improvement sector is no exception. At Kingfisher, our retail banners include B&Q, Castorama, Brico Dépôt, and Screwfix, and our customers expect a seamless shopping experience whether they shop with us online or in store.
From product recommendations to delivery suggestions to location-based services, the technology required to meet these changing expectations is all powered by data. And to effectively deliver for our customers, that data needs to be highly available, highly accurate, and highly optimized. It needs to be gold standard.
In November 2022, we signed a five-year strategic partnership with Google Cloud to accelerate the migration of our huge on-premises SAP workloads to the cloud. By moving away from a tightly coupled, monolithic architecture, our goal was to improve our resilience and strengthen our data platform to unleash the full potential of our data, giving us the resilience and agility we need to power our growth.
Data speed and quality are critical to helping us achieve our goals, with data platforms, recommendation engines, sophisticated machine learning, and the ability to quickly ingest and curate content, all key to our future plans. Partnering with Google Cloud helps us to unlock this potential, with Google Cloud Marketplace also offering a critical capability to help us simplify procurement.
One of the most important factors in our decision to partner with Google Cloud was the expertise. Google Cloud not only brings a specific set of functionality and services that are well suited to our needs, but a team of people behind those solutions who understand our industry. They know our needs and goals, and can help us work through our challenges. And as we continue to migrate our workloads and build our architecture, the Google Cloud team is fully engaged, working closely with us in a meeting of minds.
This partnership has already started to deliver results. By abstracting the data away from our core platform, we are now able to use it more productively for our business needs, and we’re currently working on some use cases around supply chain visibility. One such project enables us to dynamically price products according to various live promotions, so that we can react to the market with more agility.
This is only possible because we’ve been able to separate the data from our SAP system and run it through Google Cloud solutions such as BigQuery and Cloud Storage, enabling us to provide a more personalized shopping experience. Plans are now underway to use our product and sales data to create a new, real-time order system to greatly improve stock accuracy, as well as scaling up B&Q’s online marketplace from 700,000 products to 4 million (Kingfisher’s H1 2023/23 Financial Results).
The future of digital retail is highly compute-intensive, requiring a level of real-time data processing near equivalent to that needed to power a major stock market. Working with Google Cloud gives us the processing power to use our data to its full potential, freeing us to focus on what we do best: offering the best home improvement proposition to our customers.
The growing suite of AI solutions in Google Cloud adds another dimension to our ability to leverage data, which will be increasingly important to enhancing the customer experience. Vertex AI, for example, is already allowing us to optimize our product pages, so that customers can visualize products in different scenarios and make a more informed purchasing decision. Throughout the business, AI is improving and speeding up our internal processes, which ultimately allows us to better serve our customers.
It’s no secret the retail industry is evolving at pace. With Google Cloud, we now have the agility, the support, and the data platform to create more seamless customer experiences both in stores and online.
Read More for the details.
The recent boom in the AI landscape has seen larger and more complex models give rise to mind-blowing AI capabilities across a range of applications. At the same time, these larger models are driving up costs for AI compute astronomically; state-of-the-art LLMs cost tens of millions of dollars (or more) to train, with hundreds of billions of parameters and trillions of tokens of data to learn.
ML teams need access to compute that is both scalable and price-efficient. They need the right infrastructure to operationalize ML activities and enhance developer productivity when working with large models. Moreover, they must maintain guardrails for orchestration and deployment to production.
Developing, refining, optimizing, deploying, and monitoring ML models can be challenging and complex in the current AI landscape. However, the efficient orchestration, cost-effective performance, and scalability present in Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), in tandem with Weights & Biases (W&B) Launch‘s user-friendly interface, simplifies the model development and deployment process for machine learning researchers. This integration seamlessly connects ML researchers to their training and inference infrastructure, making the management and deployment of machine learning models easier.
In this blog, we show you how to use W&B Launch to set up access to either GPUs or Cloud Tensor Processing Units (TPUs) on GKE once, and from then easily grant ML researchers frictionless access to compute.
W&B is an ML developer platform designed to enable ML teams to build, track, and deploy better models faster. As the system of record for ML activities, from experiment tracking to model registry management, W&B improves collaboration, boosts productivity, and overall helps simplify the complexity of modern ML workflows.
W&B Launch connects ML practitioners to their cloud compute infrastructure. After a one-time configuration by an ML platform team, ML researchers can then select the target environment in which they want to launch training or inference jobs.
W&B Launch automatically packages up all the code and dependencies for that job and sends it to the target environment, taking advantage of more powerful compute or parallelization to execute jobs faster and at greater scale. With jobs packaged up, practitioners can easily rerun jobs with small tweaks, such as changing hyperparameters or training datasets. ML teams also use W&B Launch to automate model evaluation and deployment workflows to manage shared compute resources more efficiently.
“We’re using W&B Launch to enable easy access to compute resources to dramatically scale our training workloads,” said Mike Seddon, Head of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence at VisualCortex. “Having that ability to create queues to each cluster and activate them is exactly what we want to do.”
GKE offers a fully-managed environment for deploying, managing, and scaling containerized applications using Kubernetes. ML teams often choose GKE over managing an open-source Kubernetes cluster because it provides the industry’s only fully managed Kubernetes with a 99.9% Pod-level SLA backed by Google SREs, which reduces operational overhead and can improve an organization’s security posture.
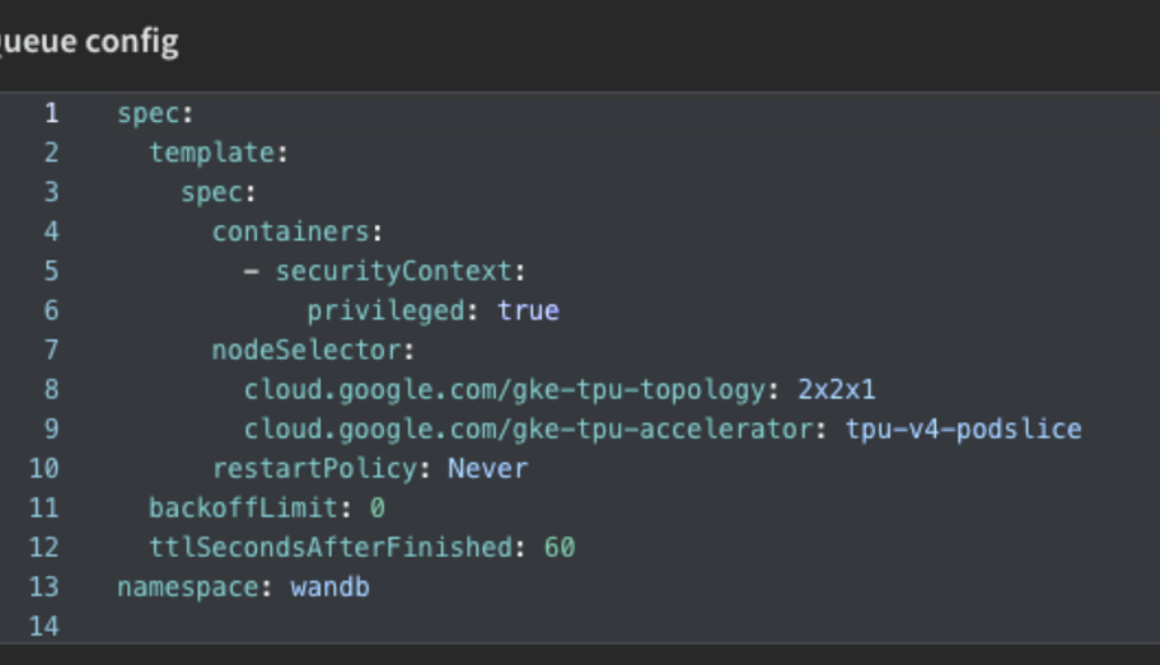
To start using W&B Launch with GKE, create a GKE cluster with TPUs or with GPUs
The W&B Launch agent builds container images inside of GKE, capturing all the dependencies for that particular run.
Once W&B Launch is configured with the GKE cluster, ML engineers can easily start training jobs by accessing powerful GPUs or Google Cloud TPUs to accelerate and supercharge AI development.
To get started, create an account, install W&B and start tracking your machine learning experiments in minutes. You can then set up your W&B Launch queue and W&B Launch agent on your GKE cluster.
W&B Launch queues must be configured to point to a specific target resource, along with any additional configuration specific to that resource. A Launch queue that points to a GKE cluster would include environment variables or set a custom namespace for its Launch queue configuration. When an agent receives a job from a queue, it also receives the queue configuration.
Once you’ve created your queue, you can set up your W&B Launch agent, which are long running processes that poll one or more W&B Launch queues for jobs, in a first in first out (FIFO) order. The agent then submits the job to the target resource — your Cloud TPU nodes within your GKE cluster — along with the configuration options specified.
Check out our documentation for more information on setting up your GKE cluster and agent.
Now that W&B Launch is set up with GKE, job execution can be handled through the W&B UI.
Identify the previously executed training run that has been tracked in W&B.Select the specific code version used for the job under the version history tab.You will see the W&B Launch button on the upper right hand corner of the Python source screen.After clicking on the W&B Launch button, you’ll be able to change any parameters for the experiment, and select the GKE environment under the “Queue” menu.
A common use case for W&B Launch is to execute a number of hyperparameter tuning jobs in parallel. Setting up a hyperparameter sweep is simple: select “Sweep” on the left-hand toolbar, enter the range of the sweep for the hyperparameters, and select the “GKE” queue for the environment.
W&B Launch with GKE is a powerful combination to provide ML researchers and ML platform teams the compute resources and automation they need to rapidly increase the rate of experimentation for AI projects. To learn more, check out the full W&B Launch documentation and this repository of pre-built W&B Launch jobs.
Read More for the details.

Making your customers and employees happy is more than just a nod to good service, it’s the name of the game. And to achieve this, many organizations are investing in digital signage and kiosk solutions to help transform customer and employee experiences. In fact, a recent IDC study found that ChromeOS devices drove 40% improved customer satisfaction and a 37% increase in employee retention for kiosk and digital signage.1 Unfortunately, many alternative kiosk and digital signage solutions in use today are expensive, clunky, and hard to maintain. And these issues are apparent no matter where you deploy devices, from retail stores and warehouses to schools and hospitals. Here’s the good news: we’re expanding our device portfolio to deliver the best kiosk, digital signage, and shared workstation experiences, and the solution may be smaller than you think.
Collaborating with our partners
ChromeOS is excited to collaborate with Lenovo to launch the first compact Chromebox for organizations worldwide. With the Lenovo Chromebox Micro, you now have a pocket-sized, cost-effective, and energy-efficient mini-computer and media player to power your kiosk and digital signage, giving your customers memorable experiences and your employees a better workday.
Small but mighty
The Lenovo Chromebox Micro has a footprint about as small as a Google Pixel, and is designed to help you deliver exceptional end-user experiences. With the ability to stream 4K video, share web-based content 24/7, and power touchscreen kiosk experiences, the Lenovo Chromebox Micro brings a big impact in a package that offers both flexibility across use cases and convenience. It’s low maintenance and enterprise-grade thanks to fanless and ventless metal construction, Intel-based to ensure speed and efficiency, and all powered via USB Type C. Its small size means it can be easily mounted anywhere, including behind large-format displays, putting your content front-and-center, not the hardware.
Lenovo Chromebox Micro isn’t just a great piece of hardware, it also brings the ChromeOS features you know and love to your kiosk and digital signage devices. Access to the Google Admin console makes it easy to deploy, troubleshoot, and monitor your devices, while the Titan-C security chip provides top-notch security, with no reported ransomware attacks or viruses.* Chrome Remote Desktop allows you to monitor, troubleshoot, and control devices from anywhere. Google engineers have worked closely with the developers of key industry solutions to make sure they work effortlessly with the Lenovo Chromebox Micro through Chrome Enterprise Recommended.
Get started today
Enhancing your customer and employee experiences doesn’t need to be difficult.
We’re passionate about providing quick-and-easy deployment of high-quality kiosk and digital signage solutions that improve employee and customer experiences. Drive big results in a small-package with the new Lenovo Chromebook Micro. Plus, there is more to come, we’re partnering with additional device manufacturers to bring affordable, compact, enterprise-grade Chromeboxes to your business soon.
Take a minute to learn more about the Lenovo Chromebox Micro today by getting in touch with our team.
*As of December 2023 there has been no evidence of any documented, successful virus attack or ransomware attack on ChromeOS. Data based on ChromeOS monitoring of various national and internal databases.
Read More for the details.

Climate change is a serious threat that is already affecting people’s health in many ways. In fact, the health of about 3.3 to 3.6 billion people is highly vulnerable to climate change thanks to more frequent and intensifying weather and climate events such as dust storms and wildfires, which contribute to air pollution.
Shockingly, 7 million people die prematurely each year due to exposure to air pollution, making it one of the greatest environmental risks to health. Despite its severe consequences, especially concerning respiratory and cardiovascular issues, air pollution often fails to garner the attention it urgently requires.
Air pollutants recognize no borders, traveling across nations and affecting air quality and ecosystems beyond their origin. While the problem is global, it disproportionately afflicts areas with fragile health infrastructures, primarily in developing countries, as highlighted by the World Health Organization (WHO).
The first-ever COP28 Health Day puts a spotlight on the pressing climate-health crisis, underscoring the necessity for adaptation solutions through both individual and collective actions. At Google Cloud, we believe that technology such as the Environment APIs from Google Maps Platform can play a crucial role. Public health decision-makers, governments and municipalities, and companies, can use it to create awareness and provide guidance, tools, and advice concerning health issues linked to air pollution. Read on for some recent examples.
Public involvement is crucial in influencing governments to adopt policies promoting climate resilience and sustainability, particularly in urban areas facing severe challenges regarding transportation, waste, and pollution. As cities grow, addressing these issues becomes more complex, making municipal decision makers key players in driving change through awareness and sustainable behavior promotion.
To get the public involved, you need to raise awareness about the serious threat of air pollution, which is not always visible to the naked eye. ‘Toxic Toby’, a London roadside memorial highlighting deaths from air pollution, is a great example of how air quality data was used in a public health campaign to raise awareness about its harmful effects. A robotic teddy bear placed on London’s streets collected real-time, location-based air quality data. Whenever pollution levels rose to dangerous levels, Toby would cough and broadcast warnings to local policymakers’ social media accounts, prompting legislative action and educational initiatives.
Similarly, seeing air pollution as a key public health issue, officials in Paris sought to establish new pollution-free open spaces and travel routes for pedestrians, bikers, and cyclists. The campaign measured the impact of road traffic, stop lights, and bus and metro stations on dynamic pollution throughout the day to inform city planning efforts and optimize traffic movement. Using air quality data integration and AI-driven analysis, the campaign provided Parisians with real-time actionable health-focused recommendations, as well as access to pollution exposure information with a personal health risk score.
By having access to environmental data and insights, governments obtain a better understanding of the health hazards affecting their communities. They can then use this information to inform policies and monitor their effectiveness. This data can also be used in educational campaigns aimed at protecting peoples’ health and well-being.
By becoming a dependable source of key environmental insights, governments, municipalities, and health organizations can positively impact citizens’ lives by helping them make healthier daily decisions. With air quality data, they can provide heatmaps, share in-depth pollutant details, and make recommendations to assist people in minimizing exposure to air pollution — even when it comes to hyperlocal questions such as which park to go to, whether or not to exercise outside, when to open windows, and when to activate air purifiers and stay indoors.
For example, the Google.org funded AirQo hopes to assist African citizens to take effective action to limit exposure and reduce air pollution. To do this they place low-cost air quality monitors throughout city infrastructure and use Google Cloud-based AI software to analyze air quality and predict local pollution in the next few days — providing locally-led solutions to Africa’s air pollution challenges.
Google is focused on empowering individuals with better information when they’re looking to make decisions that can drive positive action for people and our planet. We strive to empower everyone with technology and innovations that support adaptation solutions to address the climate change health crisis with environmental products like our Air Quality API and Pollen API from Google Maps Platform.
To learn more about Google’s work to improve public health in light of the climate crisis, visit google.sustainability. We’ll be blogging throughout COP28; follow along here.
Read More for the details.

As COP28 kicks off, it is clear we have a lot more to do in both raising ambitions and taking action. The latest United Nations analysis finds current emissions pledges likely mean warming of nearly three degrees Celsius this century. That translates to rapidly escalating hazards, such as floods, fire, and loss of farmland, worldwide. And this warming could be substantially higher if these pledges aren’t met.
So what do we do? The UN calls for urgent acceleration of low-carbon transformations, especially in high-income, high-emitting countries, and this is where Google has a unique opportunity to help.
At Google, we believe that climate change is one of the most urgent and critical collective challenges facing the world today. And we’re helping in many ways. We remain unwavering in our commitment to the Paris Agreement and the urgency to chart a sustainable course, or face the worst consequences of climate change.
It’s why we’re pursuing net-zero emissions across our operations and value chain by 2030, supported by an ambitious clean energy goal to run on 24/7 carbon-free energy on every grid where we operate. That’s good news for billions of consumers and users who search, use Gmail, store photos, or use Google products to do business.
Our commitment extends to our customers and partners, too. Google Cloud recognizes the potential of cloud and AI to play an essential role in cutting carbon whilst helping companies drive efficiency and green growth. A recent report released by Google with BCG suggests that AI has the potential to mitigate 5-10% of global greenhouse gas emissions by 2030. 5% is equivalent to a third of the emissions of the whole of the USA.
In support of the COP28’s presidency’s goal of an accelerated transition, we are focused on three areas: improving access to data about the climate transition, building the climate tech ecosystem, and unlocking the potential of geospatial analytics for climate resilience.
Today, climate transition data, including key data on company greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and emission reduction targets, is not reported consistently, and there are often barriers to accessing this information. Furthermore, actionable insights into where companies can reduce emissions and drive ROI are also difficult to obtain.
That is why we are excited to be involved in the creation of the Net Zero Public Data Utility being launched by Michael Bloomberg at COP28.
The Net-Zero Data Public Utility (NZDPU) aims to become a global, centralized, and open repository for data related to climate transition in the private sector — freely available to all stakeholders. Participants will be able to easily access and interpret a core set of company-level climate transition related data, a critical step in realising the net-zero transition. The NZDPU RFP process led to the selection of Google, Insomniac Design Inc, and CyBourn Inc. to design and build the NZDPU proof of concept being launched at COP28.
We are committed to supporting the growing ecosystem of climate tech entrepreneurs and startups who are harnessing cloud and AI to drive impact.
A key part of this is the Google Cloud Ready – Sustainability (GCR-S) validation initiative, which can help accelerate the sustainability transition for all our customers. Already, forty climate tech partners with the GCR-S designation are now building their solutions on Google Cloud to reduce carbon emissions, increase the sustainability of value chains, help organizations manage their climate data, or identify climate risks for increased resilience. We look forward to combining cloud technologies and connectivity to partners across the Google Cloud ecosystem to support innovative climate tech vendors accelerate their growth.
Finally, we’re focusing on the physical impacts of climate. There’s huge potential for geospatial analytics to support adaptation to climate risks — especially in increasing resilience.
Geospatial analytics can help organizations improve their understanding of the impact of climate change on their business infrastructure and supply chains. Through the power of Google Earth Engine, BigQuery and Vertex AI, Google Cloud and its partners are bringing visibility to both near-term acute risks and longer-term chronic climate risks.
For example, Climate Engine, a Google Cloud Ready – Sustainability partner, has launched SpatiaFi on Google Cloud. Together with Deloitte, Google Cloud and Climate Engine helped UK bank NatWest explore the use of its satellite-data archive in conjunction with Climate Engine’s SpatiaFi software platform. The work allowed NatWest to understand the role that geospatial data can play in capturing key climate-related data points for their agriculture customers.
Similarly, during 2023 we supported the UN Race to Resilience to harness geospatial data and analytics to support improved climate resilience and adaptation. Together with Google.org, we ran a design sprint during NY Climate Week in September 2023 to explore the potential of geospatial technologies to help vulnerable communities understand the impact of climate change on their communities, and to deploy solutions to reduce these impacts. The Race to Resilience team and Google are now exploring the next phase of this project to be delivered with partners in 2024.
COP28 is about accelerating action. We are committed to bringing the power of AI and Google Cloud technologies to support organizations in measuring, optimizing and reinventing their businesses for a low-carbon economy. We will be at the heart of these new data platforms, unlocking the potential of AI and in supporting the climate tech innovators of tomorrow.
Read More for the details.

Post Content
Read More for the details.

Circles is one of the fastest-growing technology companies in Singapore and is transforming the telecommunications industry. Launched in 2014, Circles now operates across 14 markets and serves millions of customers globally.
Through our digital expertise gained from operating our own digital lifestyle telco brand, Circles.Life, we identified building the world’s first cloud-native telco-as-a-service platform as the next phase of our journey. Built for operators by operators, Circles X offers a suite of software solutions to clients aiming to launch a digital telco or expand into new markets. We launched Circles X in 2019 as a cloud-native SaaS technology platform to collaborate with telco partners and scale globally quickly and efficiently.
First launched on Circles X’s platform, we partnered with one of Indonesia’s leading mobile network operators (MNO) to launch a digital telco brand in 2020. Built natively on Google Cloud, a distributed team from India, Sri Lanka, Singapore and Indonesia brought the platform live in less than 60 days — under a third of our six-month target — even amidst the complications of the COVID-19 crisis.
To do this, we built the Circles X platform using DevOps Research and Assessment (DORA) metrics endorsed by Google Cloud. Tracking these metrics underpins the performance of our software development team, and has proved instrumental to the success of our mission. The metrics include:
Deployment Frequency: How often an organization successfully releases to productionLead Time for Changes: The amount of time it takes a commit to get into productionChange Failure Rate: The percentage of deployments causing a failure in productionTime to Restore Service: How long it takes an organization to recover from a failure in production
We decided early on to use DORA standards as a guidepost for building our solution to give us the methodologies we needed for success, and the Google Cloud team helped us every step of the way in achieving optimal outcomes following the DORA methodology. Our development team was and continues to be focused on ensuring they meet high or elite performance benchmarks for each of the DORA metrics, resulting in the nimble and timely development of our platform.
Here is a step-by-step account of how we built a world-class DORA culture throughout our organization, building upon the site reliability (SRE) practices that we absorbed from Google Cloud training and guidance protocols.
Working with the Google Cloud team, we set up a full-stack SRE team including a Developer Solution Architect and leaders in Quality Assurance, Security, SRE DevOps and Digital Data Storage.We adhered to domain-driven design, an optimal software design approach, that we combined with SRE best practices for DORA excellence. This gave the teams the freedom to independently build services and deliver applications without legacy dependencies.Lastly, we extended the structure not just by team, but also services and infrastructure, to be isolated for each domain. All of our DORA metrics and dashboards for internal developer experience are based on domain-driven best practices.
Adhering to DORA benchmarks, the team can roll out products and updates weekly — 75% faster than a traditional telecom operator. This year, we expect even faster deployments as we deepen our DORA expertise. Crucially, Google Cloud provided us exceptional support whenever we faced hurdles building our DORA-enabled platform strategy, whether it was technical, organizational, or cultural.
We benefited from open conversations with Google Cloud, as the team was always ready to share its feedback, comments and viewpoints. Google Cloud also helped us connect with different industry experts for key insights into architecting our solution and creating the right DORA culture.
With Google Cloud team support and focus on DORA metrics, we proved that the Circles X platform could build successful, profitable, agile, and scalable digital brands. Building on these foundations, we’re industrializing the Circles X platform to partner with a global pipeline of MNOs and help the telecom industry build brands and experiences that delight digitally-savvy customers.
In the two years since it launched, Indonesia’s digital brand has grown into one of the most popular and fastest-growing digital telcos in Indonesia. Our DORA learnings have been essential for our future plans of telco empowerment around the world. Moreover, Google Cloud gave us the world-class continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) we need to build a reliable software development and testing practice that would allow us to launch within six months, from early iterations gradually up to our current version of the digital telco brand.
This was made possible with the infrastructure-as-code approach enabled by Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), and other key managed services such as Cloud SQL, DataProc, Filestore, Cloud CDN, Pub/Sub and Cloud Storage. Building Indonesia’s favorite digital brand on GKE saved significantly on costs, eliminated dependencies and improved developer efficiency and deployment frequency to go to market. As a result, we are the first telco in Indonesia to have an on-demand developer environment in production, where we can spin up a GKE environment within just a few minutes. This has brought us competitive advantage, increasing developer productivity by 40% and reducing deployment frequency to days from weeks.
Building on the success of the digital brand in Indonesia, we are partnering with Google Cloud to transform our Circles X platform into a robust, flexible solution that enables rapid global launch and expansion for our partner MNOs.
Read More for the details.
YugabyteDB, a distributed SQL database, when combined with BigQuery, tackles data fragmentation, data integration, and scalability issues businesses face.
It ensures that data is well-organized and not scattered across different places, making it easier to use in BigQuery for analytics. YugabyteDB’s ability to grow with the amount of data helps companies handle more information without slowing down. It also maintains consistency in data access, crucial for reliable results in BigQuery’s complex queries. The streamlined integration enhances overall efficiency by managing and analyzing data from a single source, reducing complexity. This combination empowers organizations to make better decisions based on up-to-date and accurate information, contributing to their success in the data-driven landscape.
BigQuery is renowned for its ability to store, process, and analyze vast datasets using SQL-like queries. As a fully managed service with seamless integration into other Google Cloud Platform services, BigQuery lets users scale their data operations to petabytes. It also provides advanced analytics, real-time dashboards, and machine learning capabilities. By incorporating YugabyteDB into the mix, users can further enhance their analytical capabilities and streamline their data pipeline.
YugabyteDB is designed to deliver scale, availability and enterprise-grade RDBMS capabilities for mission-critical transactional applications. It is a powerful cloud-native database that thrives in any cloud environment. With its support for multi-cloud and hybrid cloud deployment, YugabyteDB seamlessly integrates with BigQuery using the YugabyteDB CDC Connector and Apache Kafka. This integration enables the real-time consumption of data for analysis without the need for additional processing or batch programs.
Integrating YugabyteDB with BigQuery offers numerous benefits. Here are the top six.
Real-time data integration: YugabyteDB’s Change Data Capture (CDC) feature synchronizes data changes in real-time between YugabyteDB and BigQuery tables. This seamless flow of data enables real-time analytics, ensuring that users have access to the most up-to-date information for timely insights.Data accuracy: YugabyteDB’s CDC connector ensures accurate and up-to-date data in BigQuery. By capturing and replicating data changes in real-time, the integration guarantees that decision-makers have reliable information at their disposal, enabling confident and informed choices.Scalability: Both YugabyteDB and BigQuery are horizontally scalable solutions capable of handling the growing demands of businesses. As data volumes increase, these platforms can seamlessly accommodate bigger workloads, ensuring efficient data processing and analysis.Predictive analytics: By combining YugabyteDB’s transactional data with the analytical capabilities of BigQuery, businesses can unlock the potential of predictive analytics. Applications can forecast trends, predict future performance, and proactively address issues before they occur, gaining a competitive edge in the market.Multi-cloud and hybrid cloud deployment: YugabyteDB’s support for multi-cloud and hybrid cloud deployments adds flexibility to the data ecosystem. This allows businesses to retrieve data from various environments and combine it with BigQuery, creating a unified and comprehensive view of their data.
By harnessing the benefits of YugabyteDB and BigQuery integration, businesses can supercharge their analytical capabilities, streamline their data pipelines, and gain actionable insights from their large datasets. Whether you’re looking to make data-driven decisions, perform real-time analytics, or leverage predictive analytics, combining YugabyteDB and BigQuery is a winning combination for your data operations.
YugabyteDB’s Change Data Capture (CDC) with BigQuery serves multiple essential use cases. Let’s focus on two key examples.
1.Industrial IoT (IIoT): In IIoT, streaming analytics is the continuous analysis of data records as they are generated. Unlike traditional batch processing, which involves collecting and analyzing data at regular intervals, streaming analytics enables real-time analysis of data from sources like sensors/actuators, IoT devices and IoT gateways. This data can then be written into YugabyteDB with high throughput and then streamed continuously to BigQuery Tables for advanced analytics using Google Vertex AI or other AI programs.
Examples of IIoT Stream Analytics
BigQuery can process and analyze data from industrial IoT devices, enabling efficient operations and maintenance. Two real-world examples include:
Supply chain optimization: Analyze data from IoT-enabled tracking devices to monitor inventory, track shipments, and optimize logistics operations.Energy efficiency: Analyze data from IoT sensors and meters to identify energy consumption patterns to optimize usage and reduce costs.
2. Equipment predictive maintenance analytics: In various industries such as manufacturing, telecom, and instrumentation, equipment predictive maintenance analytics is a common and important use case. YugabyteDB plays a crucial role in collecting and storing equipment notifications and performance data in real time. This enables the seamless generation of operational reports for on-site operators, providing them with current work orders and notifications.
Maintenance analytics is important for determining equipment lifespan and identifying maintenance requirements. YugabyteDB CDC facilitates the integration of analytics data residing in BigQuery. By pushing the stream of notifications and work orders to BigQuery tables, historical data accumulates, enabling the development of machine learning or AI models. These models can be fed back to YugabyteDB for tracking purposes, including failure probabilities, risk ratings, equipment health scores, and forecasted inventory levels for parts. This integration not only enables advanced analytics but also helps the OLTP database (in this case, YugabyteDB) store the right data for the site engineers or maintenance personnel in the field.
So now let’s walk through how easy it is to integrate YugabyteDB with BigQuery using CDC.
The diagram below (Figure 1) shows the end-to-end integration architecture of YugabyteDB to BigQuery.
Figure 1 – End to End Architecture
The table below shows the data flow sequences with their operations and tasks performed.
Note: Link for creating the stream ID mentioned in #1
1. Set up BigQuery Sink
Install YugabyteDB
You can deploy YugabyteDB available on Google Cloud Marketplace using this link. Alternatively, there are other options to install or deploy YugabyteDB. If you are running in Windows, you can leverage Docker on Windows with YugabyteDB.
Install and set up YugabyteDB CDC and Debezium connector
Ensure YugabyteDB CDC is configured to capture changes in the database and is running (as per the above architecture diagram) along with its dependent components. You should see a Kafka topic name and group name as per this document; it will appear in the streaming logs either through CLI or via Kafka UI (e.g. if you used KOwl).
Download and configure BigQuery Connector
Download the BigQuery Connector . Unzip and add the JAR files to YugabyteDB’s CDC (Debezium Connector) Libs folder (e.g. /kafka/libs). Then restart the Docker container
Set up BigQuery in Google Cloud
Setting up BigQuery in Google Cloud benefits both developers and DBAs by providing a scalable, serverless, and integrated analytics platform. It simplifies data analytics processes, enhances collaboration, ensures security and compliance, and supports real-time processing, ultimately contributing to more effective and efficient data-driven decision-making.
Follow these five steps to set up BigQuery in Google Cloud.
Create a Google Cloud Platform account. If you don’t already have one, create a Google Cloud Platform account by visiting the Google Cloud Console and following the prompts.Create a new project (if you don’t already have one). Once you’re logged into the Google Cloud Console, create a new project by clicking the “Select a Project” dropdown menu at the top of the page and clicking on “New Project”. Follow the prompts to set up your new project.Enable billing (if you haven’t done it already). NOTE: Before you can use BigQuery, you need to enable billing for your Google Cloud account. To do this, navigate to the “Billing” section of the Google Cloud Console and follow the prompts.Enable the BigQuery API: To use BigQuery, you need to enable the BigQuery API for your project. To do this, navigate to the “APIs & Services” section of the Google Cloud Console and click on “Enable APIs and Services”. Search for “BigQuery” and click the “Enable” button..Create a Service Account and assign BigQuery roles in IAM (Identity and Access Management): As shown in Figure 4, create a service account and assign the IAM role for Big Query. The following roles are mandatory to create a BigQuery table:BigQuery Data EditorBigQuery Data Owner
Figure 2 – Google Cloud – Service Account for BigQuery
After creating a service account, you will see the details (as shown in Figure 3). Create a private and public key for the service account and download it in your local machine. It needs to be copied to YugabyteDB’s CDC Debezium Docker container in a designated folder (e.g., “/kafka/balabigquerytesting-cc6cbd51077d.json”). This is what you refer to while deploying the connector.
Figure 3 – Google Cloud – Generate Key for the Service Account
2. Deploy the configuration for the BigQuery connector
Source Connector
Create and deploy the source connector (as shown below), change the database hostname, database master addresses, database user, password, database name, logical server name and table include list and StreamID according to your CDC configuration (refer code block highlighted in yellow).
Target Connector (BigQuery Connector):
The configuration below shows a sample BigQuerySink connector. The topic name, Google project, dataset name, default dataset name — highlighted in yellow — need to be replaced according to your specific configuration.
The key file fields contain the private key location of your Google project, and it needs to be kept in the YugabyteDB’s CDC Debezium Docker connector folder. (e.g. /kafka)
3. Output in BigQuery Console
After deployment, the table name (e.g. dbserver11_public_testcdc) will be created in BigQuery automatically (see below).
Figure 4 – Data stored in the BigQuery Table
Figure 5 – BigQuery – Execution Details for a sample BigQuery table is shown below.
Figure 6 – Query Execution Details
Following the steps above is all it takes to integrate YugabyteDB’s CDC connector with BigQuery.
Combining YugabyteDB OLTP data with BigQuery data can benefit an application in a number of ways (e.g. real-time analytics, advanced analytics with machine learning, historical analysis and data warehousing and reporting). YugabyteDB holds the transactional data that is generated by an application in real-time, while BigQuery data is typically large, historical data sets that are most often used for analysis. By combining these two types of data, an application can leverage the strengths of both to provide real-time insights and support better, quicker, more accurate and informed decision-making.
Next steps:
Discover more about YugabyteDBDive into distributed SQL with Distributed SQL for DummiesReady to give it a try? Procure YugabyteDB through Google Cloud Marketplace, and build your first geo-distributed application.
Read More for the details.

The holiday season is upon us and 2024 is just around the corner. Generative AI has been a hot topic of conversation this year, so throughout December join us for 12 days of no-cost generative AI training to build your skills and knowledge.
Give yourself the gift of learning. Check out our featured gen AI learning content in the form of on-demand courses, labs and videos to help validate your AI know-how into the New Year and beyond. These gen AI trainings are no-cost to watch and complete, no matter when you complete them this month.
Designed for any role or skill set, these learning opportunities will help you understand what generative AI is, how it can be used and how it is different from other types of machine learning. No technical experience needed.
Generative AI, explained – What even is generative AI? Hear guesses from people on the street and unwrap the laughs (there were some funny responses), and get a quick high-level description in this 60 second video.Introduction to Generative AI – This 22 minute course includes a video, reading material, and a quiz to test your knowledge. You’ll learn about the fundamentals of AI and Google Cloud tools to help you develop your own gen AI apps.Introduction to Large Language Models – When you complete this course, you’ll have a foundational understanding of large language models (LLMs), use cases, and how you can use prompt tuning to enhance LLM performance. The course and follow-up quiz should take about 30 minutes to finish.Generative AI Fundamentals Skill Badge – Complete three foundational-level courses and a quiz to earn a shareable Google Cloud skill badge to demonstrate your understanding of fundamental gen AI concepts.What is Generative AI Studio? – Check out this quick video to learn how you can use Generative AI Studio. Hint: anyone can try it, even without any code!Introduction to Generative AI Studio – Generative AI helps users prototype and customize models for use in applications. In this short video, you’ll learn about Generative AI Studio’s features, options, and uses in a product demo format.Introduction to Image Generation – In this video, learn about diffusion models — a family of machine learning models that can be used in image generation — that can be trained and deployed on Vertex AI. It’s a quick view to help you learn in a flash.Introduction to Responsible AI – In this video you’ll get an overview of responsible AI and how Google implements responsible AI into our products.Responsible AI: Applying AI Principles with Google Cloud – Learn how to operationalize responsible AI in your organization in this set of video courses.
Are you an application developer, database engineer, integration engineer, or security engineer? Then check out these technical training options below.
10. The Arcade – Get hands-on knowledge in the Google Cloud environment by completing generative AI labs for no-cost through this gamified experience. Bonus: you’ll accumulate points to earn Google Cloud swag. Game on!
11. Gen AI Bootcamp – Gen AI Bootcamp is a series of workshops available on-demand. You’ll progress from foundational to advanced topics. Practitioners can follow start-to-finish, and experienced Gen AI developers can jump straight into the more advanced sessions.
12. What is Codey? Learn in 60 seconds – Come up with an idea… and then code it! Learn how Codey helps write code, even for beginners. It only takes a minute to find out how.
For these and all our generative AI training content, visit Google Cloud Skills Boost.
Read More for the details.
