GCP – Palo Alto Networks automates customer intelligence document creation with agentic design
For a global cybersecurity leader like Palo Alto Networks, a comprehensive understanding of each customer is critical for success. For every engagement the Palo Alto Networks pre-sales team has, the comprehensive understanding is centralized in an internal Document of Record (DOR), a vital asset that provides a 360-degree standardized view of the customer for sales and support teams.
The Challenge: A manual, time-intensive process
Historically, creating a DOR was a manual process that required significant effort from highly skilled employees.
The task involved:
-
Gathering data from Salesforce.
-
Searching through extensive internal knowledge bases spread across multiple systems.
-
Synthesizing the information into a structured document.
This process could take days, delaying the opportunity to be won and closed, while diverting valuable time from experts who could otherwise be focused on customer-facing strategic work. To address this inefficiency, Palo Alto Networks sought to automate the entire workflow using a sophisticated AI agent built on Google Cloud.
An automated, agent-driven workflow
Palo Alto Networks developed an AI agent using Google’s open-source Agent Development Kit (ADK) to autonomously generate the DOR. The required DOR questions are answered by utilizing GCP resources like Vertex AI RAG Engine, Vertex AI Discovery Engine Search (Google’s Enterprise search platform). The agent is deployed on Vertex AI Agent Engine, a fully managed platform that provides the necessary scalability and reliability for this business-critical task, while providing out-of-box session and memory handling.
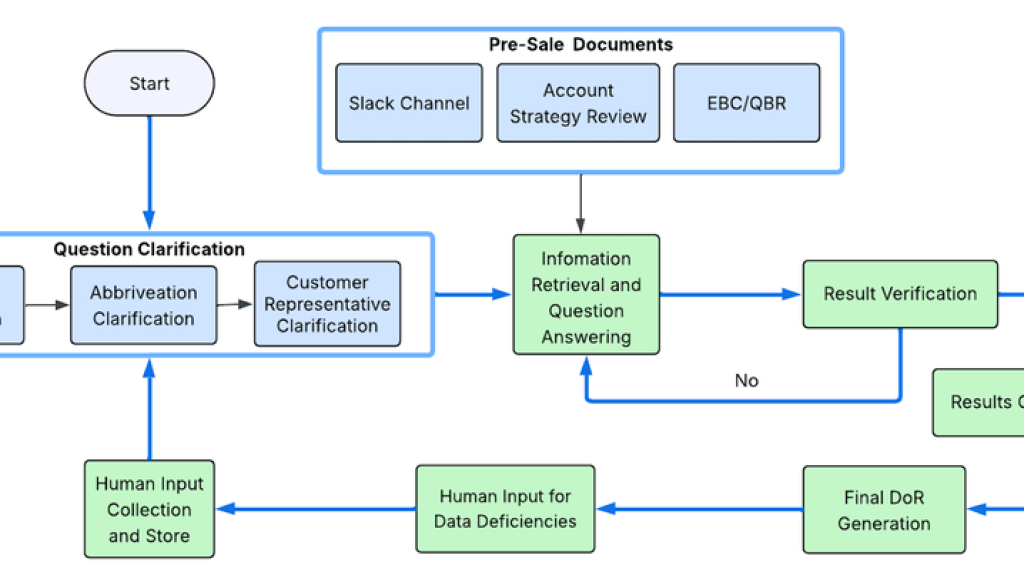
Deployment architecture
The system’s architecture is composed of the following core elements:
-
Two AI Agent Engine endpoints: These agents, deployed on Vertex AI Agent Engine, serve as API endpoints. They process POST requests from the Salesforce portal and return results, leveraging the managed scalability of Agent Engine for a distributed approach.
-
Webserver (FastAPI on GKE): Built with FastAPI and hosted on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), this web server orchestrates the system. It initiates requests to the Agent Engine endpoints, validates their responses, and stores the processed data.
-
Vertex AI Rag Engine: This acts as a serving datastore, providing the two AI agents with access to documents and logs uploaded to Google Cloud Storage (GCS).
The automated process steps
The automated workflow is a seven-step process, orchestrated by a central webserver, that seamlessly integrates Salesforce, Google Cloud AI services, and internal data sources.
-
Initiation from Salesforce: The process begins when a request for a specific customer account is triggered within Salesforce. This request is sent to a FastAPI webserver hosted on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE).
-
Metadata Retrieval and Question Preparation: The webserver receives the request, retrieves the relevant customer metadata from Salesforce, and prepares a predefined list of over 140 standard questions designed to build a comprehensive customer profile.
-
Parallel Processing for Efficiency: To ensure the AI agent can scale and to optimize for speed, the webserver sends the questions to the Vertex AI Agent Engine endpoint in batches of five. This multi-threaded approach allows the Agent Engine to horizontally scale and process multiple questions concurrently – leveraging the managed auto-scale nature of Agent Engine.
-
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and Vertex Discovery Engine: Each question is enhanced and clarified for enriching relevant context, which is achieved by pre-processing using Gemini 2.5 flash. It is then sent to two different agents, which then query their respective knowledge bases. This service acts as the RAG engine, searching a vast corpus of internal company documents and logs that were uploaded as part of briefing, to find and return only the most relevant snippets of information, grounding the agent’s responses in factual, company-approved data.
-
LLM-Powered Answer Synthesis: The data snippets retrieved by Vertex AI Search are passed to a Gemini model, which synthesizes the information into a high-quality, coherent answer.Each agent independently to answer the questions and assigns a relevance score to its respective answer. Relevance score here measures the proportion of the claims in the answer that are grounded in the facts . he system then reconciles these answers with respect to the relevance score, selecting the best response and storing it as the definitive truth before moving to the next question. In addition, a verification step is performed. This step assesses the groundedness of the claims made in the final answer and categorizes the final answer into low, medium, or high confidence, allowing the end user to make the final call .
-
Stateful Orchestration: The FastAPI webserver manages the entire operation, storing the results and maintaining the state of the running process. It tracks which questions have been answered and consolidates the final document.
- Asynchronous Handoff to Salesforce: Once all questions are answered, the webserver publishes the completed DOR to a Cloud Pub/Sub topic. This creates a reliable, asynchronous handoff. A separate service consumes the message from the topic and writes the final document back into the appropriate record in Salesforce, completing the workflow.

The technology stack
This solution effectively combines Google Cloud’s managed AI services with open-source frameworks:
-
Agent Development Kit (ADK): The open-source Python framework used to define the agent’s complex logic, including the multi-step orchestration, state management, and integration with various services.
-
Vertex AI Agent Engine: The fully managed, serverless environment that hosts and executes the ADK-based agent, handling scaling, security, and operational overhead.
-
Vertex AI RAG Engine: For generating contextually grounded responses. The Engine is configured to use Vertex AI Search as its retrieval backend, efficiently pulling relevant information from our internal documents to inform the language model.
-
Gemini Models: Provides the advanced reasoning and language synthesis capabilities required to generate high-quality, human-readable answers from the retrieved data.
-
Cloud Pub/Sub: Functions as a durable messaging queue that decouples the agent from the final write-back process, increasing the overall resilience and reliability of the architecture.
-
Cloud Storage: Served as storage for the unstructured customer documents needed to answer the DOR questions.
Overcoming challenges
The journey to automate DOR creation with an AI agent was not without its hurdles. Several key challenges were encountered and successfully addressed, highlighting important architectural and deployment considerations for similar agentic AI solutions.
1. Agent context management and scaling:
Initially, the design involved passing all 140+ questions to the agent at once, expecting it to iterate and manage its progress. However, this approach led to significant memory overloads and “Out of Memory” (OOM) errors. The agent’s internal context window, which grew with each check against its logic and the accumulation of answers, quickly became unmanageable.
The solution involved shifting the responsibility for state management to a FastAPI server acting as an orchestrator. Instead of receiving all questions upfront, the agent was designed to process questions one by one. The FastAPI server now maintains the overall context and the accumulating document, passing individual questions to the agent and storing the agent’s responses. This compartmentalization of context dramatically improved the agent’s stability and allowed for more efficient scaling.
2. Deployment architecture and resource management:
Determining the optimal deployment architecture for both the backend orchestrator (FastAPI server) and the agent on Vertex AI Agent Engine posed another challenge. Early experiments with deploying both components within a single Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) cluster resulted in frequent pod crashes, primarily due to the agent’s context and memory demands. The decision was made to decouple the FastAPI server from the agent’s runtime. The FastAPI server is deployed as a standalone service on GKE, which then makes calls to the agent separately deployed on Vertex AI Agent Engine. This separation leverages Vertex AI Agent Engine’s fully managed and scalable environment for the agent, while providing the flexibility of a custom backend orchestrator.
3. Performance optimization for LLM calls:
The nature of generating answers using Gemini models, involving multiple API calls for each of the 140+ questions, initially resulted in a lengthy runtime of approximately 2.5 hours per DOR. Recognizing that these calls were I/O-bound, the process was significantly optimized through parallelization. By implementing multi-threading within the FastAPI orchestrator, multiple Gemini calls could be executed concurrently. Vertex AI Agent Engine’s horizontal scaling capabilities further supported this parallel execution. This architectural change drastically reduced the overall processing time, improving efficiency by a substantial margin.
Business outcomes
The implementation of this AI agent has delivered significant, measurable results for Palo Alto Networks:
-
Increased Efficiency: The time required to create a comprehensive DOR has been dramatically reduced.
-
Improved Consistency and Quality: By standardizing on a 140-question framework, every DOR now meets a uniform high standard of quality and completeness.
-
Enhanced Accuracy: Grounding the agent’s answers in a trusted RAG system minimizes the risk of human error and ensures the information is drawn from the latest internal documentation.
-
Strategic Re-focus of Personnel: The automation of this task allows expert employees to dedicate more time to high-value activities like customer strategy and direct engagement.
-
Ability to understand the gaps in documentation, areas where the answers are weak or absent ensures the pre-sales teams coordinating the efforts can emphasize on those topics for a more complete understanding of the customer.
This use case demonstrates a practical and powerful application of agentic AI in the enterprise, showcasing how a combination of open-source frameworks and managed cloud services can solve complex business challenges and drive operational efficiency.
The team would like to thank Googlers Hugo Selbie (GSD AI Incubation team) and Casey Justus (Professional Services) for their support and technical leadership on agents and agent frameworks as well as their deep expertise in ADK and Agent Engine.
Read More for the details.