GCP – Now available: Rust SDK for Google Cloud
Rust is gaining momentum across the cloud developer community for good reason. It’s fast, memory-safe, and built for modern systems. Until now, however, your options for integrating Rust with Google Cloud were limited to unofficial Rust SDKs, which made things harder to maintain, less secure, or were missing features.
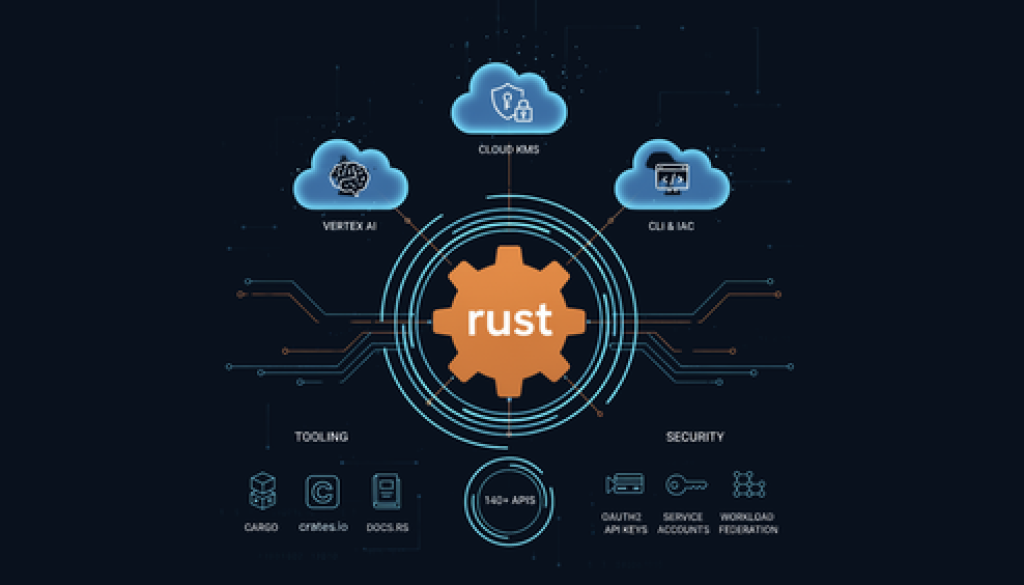
We’re excited to announce the official Rust SDK for Google Cloud, giving you a supported, idiomatic way to use Rust across more than 140+ Google Cloud APIs — no wrappers, no hacks. This SDK is built with the same commitment to consistency, security, and platform integration as our other official Google Cloud client libraries.
If you’re building high-performance backend services in Rust, writing secure, reliable data processing or real-time analytics pipelines, or maintaining internal tools that call Google Cloud APIs, this SDK makes your experience on Google Cloud much smoother.
What’s in the box?
The Google Cloud Rust SDK comes packed with features to streamline your development:
-
140+ APIs: Access client libraries covering core Google Cloud services. This includes capabilities for Vertex AI for machine learning workflows, Cloud Key Management Service for managing cryptographic keys, and Identity and Access Management for fine-grained control over your resources.
-
See the full list of packages.
-
Built-in auth: Support for Application Default Credentials (ADC), OAuth2, API Keys, service accounts, and (soon) Workload Identity Federation.
-
Helpful documentation and code samples: We’ve included guides, examples, and docs made for Rust developers.
Try the Rust SDK now!
You can find the SDK on crates.io and the source code on GitHub.
To learn more and start building, explore the official Rust SDK user guide.
Let us know what you think
We’re incredibly excited to see what you’ll build with the Rust SDK on Google Cloud! We welcome your feedback and contributions as we’re actively improving the Rust SDK.
Got feature requests? Found a bug? Want to shape what comes next? Join the discussion on GitHub.
Read More for the details.