Azure – Public Preview: Migrate virtual machine backups using standard backup policy to enhanced backup policy
Azure Backup now supports migrating virtual backups using standard backup policy to enhanced backup policy.
Read More for the details.

Azure Backup now supports migrating virtual backups using standard backup policy to enhanced backup policy.
Read More for the details.

The security of the software supply chain is a complex undertaking for modern enterprises. Securing the software supply chain, particularly build artifacts like container images, is a crucial step in enhancing overall security. To provide built-in, centralized visibility into your applications, we are introducing software supply chain security insights for your Google Kubernetes Engine workloads in the GKE Security Posture dashboard.
Our built-in GKE Security Posture dashboard can provide opinionated guidance to help improve the security posture of your GKE clusters and containerized workloads. It includes insights into vulnerabilities and workload configuration checks. The dashboard also clearly points out which workloads are affected by a security concern and provides actionable guidance to address it.
To boost transparency and control over your software supply chain, we are introducing a new “Supply Chain” card within the GKE Security posture dashboard. Now available in public preview, this powerful feature allows you to visualize potential supply chain risks associated with your GKE workloads.
In this initial launch we provide two key insights:
Outdated images: Identify all images that have not updated in the last 30 days, potentially exposing you to recent vulnerabilities.
“Latest” tag usage: Gain clarity on images still using generic “latest” tag, hindering precise version control and traceability.
Our Binary Authorization service scans your images running in GKE clusters. You can view a summary of concerns on the “Supply Chain” card and drill down for further details in the “Concerns” tab within the GKE Security Posture dashboard.
Follow these steps to view the supply chain concerns:
1. Navigate to the GKE Security Posture page in the Google Cloud console. Note: You need to enable Security Posture if you haven’t already done so.
2. On the “Supply Chain” card, click “Enable Binary Authorization API” and then click on “Enable”.
3. On the next pop-up titled “Supply Chain” and click “Enable”.
GKE Security dashboard.
4. Concerns related to “image freshness” or “latest tag” will appear in the “Supply Chain” card within 15 mins.
5. Click on a concern to view the details, “Affected Workloads” tab will show a list of workloads affected by the selected concern.
GKE Security dashboard.
This initial release to address supply chain concerns in GKE Security Posture is part of our ongoing commitment to enhancing workload security. In the coming months, we plan to introduce more sophisticated supply chain concerns that can be scanned by Binary Authorization and displayed in GKE Security Posture, further bolstering the protection and adding transparency for your application and workloads.
Ready to take advantage of the improved security experience? Learn more about Binary Authorization and GKE Security Posture dashboard.
Read More for the details.
As one of the largest banks in Indonesia and Southeast Asia, Bank Rakyat Indonesia (BRI) focuses on small-to-medium businesses and microfinance. At BRI, we established a Digital Banking Development and Operation Division to implement digital banking and digitalization. Within this division, a department we call Digital BRIBRAIN develops a range of AI solutions that span customer engagement, credit underwriting, anti-fraud and risk analytics, and smart services and operations for our business and operational teams.
Within Digital BRIBRAIN, our AI research team works on projects like the BRIBRAIN Academy — a collaborative initiative with higher education institutions that aims to nurture AI and ML in banking and finance, expand BRI’s AI capabilities, and contribute to the academic community. The program enables students from partner universities to study the application of AI in the financial sector, selecting from topics such as unfair bias and fairness, explainable AI, Graph ML, federated learning, unified product recommendations, natural language processing and computer vision.
Based on our long history and work with Google Cloud, with some Vertex AI technology implemented in other use cases, we selected its products and services to provide a sandbox environment for this research effort with partner universities. This research covers a range of use cases and concepts, including the following:
Industry-wide, banks and other financial institutions use credit scoring to determine an individual’s or organization’s credit risk when applying for a loan. Historically, this is a manual and paper-driven process that uses statistical techniques and historical data. There is considerable potential benefit to apply automation to the credit scoring process, but only if it can be done responsibly.
The use of AI in credit scoring is a noted and well-documented area of concern for algorithmic unfairness. Providers should know which variables are used in credit scoring AI models and take steps to reduce the risk of disparate model outputs across marginalized groups. To help bring the industry closer to a solution where unfair bias is appropriately mitigated, we decided to work on fairness analysis in credit scoring as one of our BRIBRAIN Academy research projects.
Fairness has different meanings in different situations. To help minimize poor outcomes for lenders and applicants, we measured bias in our models with two fairness constraints, demographic parity difference and equalized odds difference, and reduced unfair bias with post-processing and reduction algorithms. As a result, we found that the fairness of demographic parity improved from 0.127 to 0.0004, and equalized odds from 0.09 to 0.01. All of the work we have done thus far is still in the research and exploration stage, as we continue to discover the limitations that need to be navigated to improve fairness.
Historical data is used to train a model to evaluate the creditworthiness of an application. However, the lack of transparency in these data can make it challenging to understand, and the ability to help others interpret results and predictions from AI models is becoming more important.
An explanation that truly represents a model’s behavior and earns the trust of concerned stakeholders is critical. With explainable AI, we can get a deeper level of understanding of how a credit score is created. We can also use the features we built in the model as filters for different credit scoring decisions. To conduct this research collaboration, we needed to leverage a secure platform with strict access controls for data storage and maintenance.
Chatbots are computer programs that simulate human conversations, with users communicating via a chat interface. Some chatbots can interpret and process users’ words or phrases and provide instant preset answers without sentiment knowledge.
Unfortunately, responses are sometimes taken out of context because they do not recognize the relationship between words. This means we had to represent chatbot data that can learn relationships between words through preprocessing using graph representation learning. These methods help to account for linguistic, semantic, and grammatical features that other natural language processing techniques like bag-of-words (BOW) models and Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency (TF-IDF) representation cannot catch.
We built a sentiment analysis model for financial chatbot responses using graph ML, allowing us to identify which conversations are positive, neutral, or negative. This helps the chatbot avoid mistakes in categorizing user responses.
Google Cloud met our needs for these projects with infrastructure and services, such as its cloud data warehouse BigQuery and its unified machine learning (ML) development platform Vertex AI, which offers a range of fully-managed tools that enabled us to undertake our ML builds.
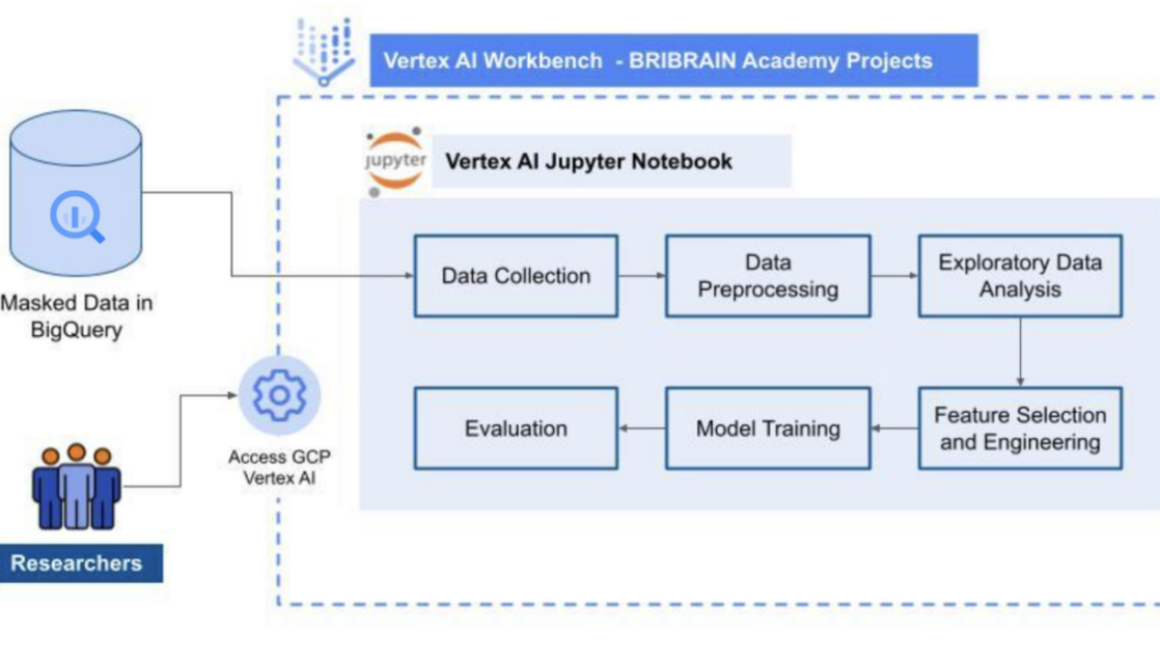
We also used Vertex AI Workbench, a Jupyter notebook-based development environment, to create and manage virtual machine instances adjusted to researchers’ needs. This enabled us to perform data preparation, model training, and evaluation of our use case model.
Using the structured data stored in BigQuery, we were able to write our own training code and train custom models through our preferred ML framework. Furthermore, we employed Identity and Access Management (IAM) to deliver fine-grained control and management of access to resources.
The general architecture we used to support each research topic is below:
We loaded masked research into BigQuery and gave researchers access to Vertex AI for specific BRIBRAIN Academy projects, assigning a virtual machine on which to conduct research. They could then use Vertex AI Workbench to perform the pipeline steps illustrated above in Vertex AI Workbench and access required data in BRIBRAIN Academy projects via BigQuery.
To build and run our ML solution efficiently and cost-effectively, we limited the resources available to each user. However, Vertex AI enabled us to modify instance resources to accommodate cases where significant data volumes were needed to create a model.
At the same time, Google Cloud data security services allowed us to protect data at rest and in transit from unauthorized access while creating and managing specific access to project data and resources. We provided specific access to researchers through BigQuery and notebook custom roles, while developers received administration roles.
With Google Cloud, Digital BRIBRAIN now has the power to explore use cases from BRIBRAIN Academy and apply lessons learned in live business projects.
For example, we have already used research around AI explainability to help us develop end-to-end ML solutions for recommender systems in our branchless banking services, known as BRILink agents. We also built a mobile application containing recommendations with AI explanations. In an environment where many users are unfamiliar with ML and its complexities, AI explainability can help make ML solutions more transparent so they can understand the rationales behind recommendations and decisions.
With our success to date, we plan to evolve our ML and data management capabilities. At present, we use BigQuery to store mostly tabular data for training and building models. Now, we are expanding these capabilities to store, process, and manage unstructured data, such as text, files and images, with Cloud Storage. In addition, we plan to monitor app usage using reports generated through Google Analytics for Firebase with some of the ML solutions available in our web-based applications.
Google Cloud gives us the ability to store our data, build and train ML model workflows, monitor access control, and maintain data security — all within a single platform. With the promising results we’ve seen, we hope to be able to tap into more of Vertex AI capabilities to support ongoing developments at BRIBRAIN Academy.
Read More for the details.
Behind every startup is a great idea — and a whole lot of documents. Paperwork for options, shares, SAFEs, etc., is arguably the most important layer for a company when it comes to tracking equity, the one source of truth that auditors and lawyers will manually process to make sure the company’s practices are in good standing and reported numbers are accurate.
But document management is a tedious process, requiring users to manually input data from files into platforms, which are often treated as separate entities, not well integrated with other business applications. Founders are familiar with this pattern: you have to read your files/documents, put the values into a platform, and then “attach a file” to start using any data-intensive and auditable platform properly. While this is great for organizing documentation next to data, traditional platforms always treat files as adjacent datasets rather than something that is integrated into the user experience.
Mantle is a next-generation equity platform for modern founders. It addresses these challenges by integrating documents and platforms, reducing the need for manual data entry. This not only saves time but also reduces the risk of human error.
Mantle uses Vertex AI to extract data from documents, enhancing the platform’s accuracy and efficiency, so users can focus on their core business activities, knowing that their equity data is accurate and up-to-date.
Data extraction techniques via Vertex AI have shortened these workflows from hours to minutes, greatly increasing the trust you have that the data you see in-platform is up-to-date and accurate.
Using Gemini, Mantle streamlines these workflows to understand the key data points in the documents. In a matter of seconds, Mantle can turn the documents in your data room into a cap table for your review and onboarding processes, alerting users when any platform values stray from the document values.
After onboarding, Mantle can “templatize” and create documents for common workflows. For special scenarios like bulk updates, it provides the ability to upload worksheets and spreadsheets to be imported and processed. This means you don’t need to transform or recreate your worksheet into a specific format for the platform.
The Mantle process unfolds in seconds. It can classify documents, and inspect documents for specific insights. Things like purchase amounts, dates, vesting schedules, are all extracted from documents in real-time and processed. Make this feasible and manageable at scale, there’s a library to generate, experiment, and test prompts based on data definitions.
Mantle always presents document findings to the user for review and verification, giving it the feel of an assistant that is helping you do your tasks more efficiently.
Gemini is at the core of Mantle’s commitment to accuracy, privacy, and user-centric solutions, and makes Mantle the go-to platform for founders seeking efficient and reliable equity management, saving founders, lawyers, auditors, etc. time when managing company equity.
Mantle leverages Google Cloud to streamline equity management and eliminate tedious processes associated with traditional document workflows. At the heart of this partnership lie two key Google technologies: Vertex AI and Gemini.
Vertex AI: Extracting data with precision
Vertex AI, Google Cloud’s unified machine learning platform, plays a crucial role in Mantle’s data extraction process. By leveraging advanced machine learning models, Vertex AI automatically extracts key information from company documents, such as option and shareholder agreements. This removes the need for manual data entry, saving time and reducing the risk of human error.
Gemini: Transforming documents into insights
Gemini, Google’s latest large language model, takes document integration to the next level. It goes beyond simple data extraction and helps Mantle understand the context and meaning within documents. This allows Mantle to generate insights and automatically populate the platform with relevant information, such as purchase amounts, dates, and vesting schedules.
Together, Vertex AI and Gemini fuel Mantle’s innovative approach to equity management. Vertex AI extracts data, while Gemini helps transform that data into actionable insights. This combination eliminates the need for users to manually input data and interpret documents, allowing them to focus on their core business activities.
By leveraging Google Cloud technologies, Mantle offers several key benefits:
Increased efficiency: Automating data extraction and document processing saves countless hours for founders, lawyers, and auditors.
Remarkable accuracy: Vertex AI and Gemini ensure that the data in Mantle is accurate and up-to-date, eliminating the risk of human error.
Intuitive user experience: Mantle’s intuitive platform makes it easy for users to manage their equity data and access insights.
Mantle and Google Cloud are paving the way for a new era of efficiency and accuracy in equity management. By harnessing the power of AI and machine learning, Mantle empowers founders and professionals to focus on what matters most – growing their businesses.
Learn more about Google Cloud’s open and innovative generative AI partner ecosystem. To get started with Mantle, join and begin experimenting with Mantle on the Google Cloud Marketplace today!
Read More for the details.

Creating marketing campaigns is often a complex and time-consuming process. Businesses aim to create real-time campaigns that are highly relevant to customer needs and personalized to maximize sales. Doing so requires real-time data analysis, segmentation, and the ability to rapidly create and execute campaigns. Achieving this high level of agility and personalization gives businesses a significant competitive advantage.
Successful marketing campaigns have always hinged on creativity and data-driven insights. Generative AI is now amplifying both of these elements, and advancements in generative AI have the potential to revolutionize the creation of marketing campaigns. By leveraging real-time data, generative AI generates personalized content such as targeted emails, social media ads or website content that’s targeted to the situation and available images, all at scale. This is in contrast to the current state of affairs, where marketers are constrained by manual processes and have limited creative resources at their disposal.
While traditional marketing methods have their place, the sheer volume of content needed in today’s landscape demands a smarter approach. Generative AI can help marketing teams launch campaigns quickly, efficiently, and with a level of personalization that was previously impossible, leading to increased engagement, conversions, and customer satisfaction.
In this blog, we will go through the various steps of how data and marketing teams can harness the power of multimodal large language models (LLMs) in BigQuery to create and launch more effective and intelligent marketing campaigns. For this demonstration, we reference Data Beans, a fictional technology company that provides a SaaS platform built on BigQuery to coffee sellers. Data Beans leverages BigQuery’s integration with Vertex AI to access Google’s AI models like Gemini Pro 1.0 and Gemini Vision Pro 1.0 to accelerate creative workflows while delivering customized campaigns at scale.
This demonstration highlights three steps of Data Beans’ marketing launch process that leverages Gemini models to create visually appealing, localized marketing campaigns for selected coffee menu items. First, we use Gemini models to brainstorm and generate high-quality images from the chosen menu item, ensuring the images accurately reflect the original coffee items. Next, we use those same models to craft tailored marketing text for each city in their native language. Finally, this text is integrated into styled HTML email templates, and the entire campaign is then stored in BigQuery for analysis and tracking.
Step 1 and 1.1: Craft the prompt and create an image
We start the marketing campaign by creating the initial image prompt and the associated image using Imagen 2. This generates a fairly basic image that might not be totally relevant, as we have not supplied all the necessary information to the prompt at this stage.
Step 1.2. Enhance the prompt
Once we create the initial image we now focus on improving our image by creating a better prompt. To do this we use Gemini Pro 1.0 to improve on our earlier Imagen 2 prompt.
Step 1.3. Generate images from LLM-generated prompts
Now that we have enhanced prompts, we will use these to generate images. Effectively, we are using LLMs to generate prompts to feed into LLMs to generate images.
Steps 2-3. Verify images and perform quality control
We are now going to use LLMs to verify the output that was generated. Effectively, we ask the LLM to check if each of the generated images contains the food items we asked for. For example, does the image contain the coffee or food items from our prompt? This will help us not just to verify if there is something abstract, but will also help us to verify the quality of the image. In addition, we can check if the image is visually appealing — a must for a marketing campaign.
Step 4. Rank images
Now that we have gone through verification and quality control, we can choose the best image for our needs. Through clever prompting, we can use Gemini Pro 1.0 again to do this for us for the thousands of images we generated. To do this, we ask Gemini to rank each image based on its visual impact, clarity of message, and relevance to our Data Beans brand. We will then select the one with the highest score.
Step 5. Generate campaign text
Now that we have selected the best image, let’s generate the best marketing text. We are storing all the generated data in BigQuery, so we generate text in JSON format. We are generating text to incorporate promotions and other relevant items.
In addition, notice how we can use Gemini Pro 1.0 to localize the marketing messages for different countries’ native languages.
Step 6. Create an HTML email campaign
The generated artifacts are displayed as part of a web application. To simplify distribution, we need to to create an HTML email with embedded formatting as well as embedding our image. Again, we use Gemini Pro 1.0 to author our marketing text as HTML based on the images and text we created in the previous steps.
The integration of LLMs into creative workflows is revolutionizing creative fields. By brainstorming and generating numerous pieces of content, LLMs provide creators with a variety of quality images for their campaigns, speed up text generation that’s automatically localized, and analyze large amounts of data. Moreover, AI-powered quality checks ensure that generated content meets desired standards.
While LLMs’ creativity can sometimes produce irrelevant images, Gemini Pro Vision 1.0 “taste test” functionality lets you choose the most appealing results. Additionally, Gemini Pro Vision 1.0 provides insightful explanations of its decision-making process. Gemini Pro 1.0 expands audience engagement by generating content in local languages, and with support for code generation, eliminates the need to know HTML.
To experiment with the capabilities showcased in this demonstration, please see the complete Colab Enterprise notebook source code. To learn more about these new features, check out the documentation. You can also use this tutorial to apply Google’s best-in-class AI models to your data, deploy models, and operationalize ML workflows without ever having to move your data from BigQuery. Finally, check out this demonstration on how to build an end-to-end data analytics and AI application directly from BigQuery while harnessing the potential of advanced models such as Gemini. As a bonus, you’ll get a behind-the-scenes take on how we made the demo.
Googlers Luis Velasco, Navjot Singh, Skander Larbi, and Manoj Gunti contributed to this blog post. Many Googlers contributed to make these features a reality.
Read More for the details.

Knowledge Bases for Amazon Bedrock (KB) securely connects foundation models (FMs) to internal company data sources for Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), to deliver more relevant and accurate responses. We are excited to announce Guardrails for Amazon Bedrock is integrated with Knowledge Bases. Guardrails allow you to instrument safeguards customized to your RAG application requirements, and responsible AI policies, leading to a better end user experience. Guardrails provides a comprehensive set of policies to protect your users from undesirable responses and interactions with a generative AI application. First, you can customize a set of denied topics to avoid within the context of your application. Second, you can filter content across prebuilt harmful categories such as hate, insults, sexual, violence, misconduct, and prompt attacks. Third, you can define a set of offensive and inappropriate words to be blocked in their application. Finally, you can filter user inputs containing sensitive information (e.g., personally identifiable information) or redact confidential information in model responses based on use cases. Guardrails can be applied to the input sent to the model as well the content generated by the foundation model. This capability within Knowledge Bases is now available in Asia Pacific (Singapore), Asia Pacific (Sydney), Asia Pacific (Tokyo), Europe (Frankfurt), US East (N. Virginia), US West (Oregon) regions. To learn more, refer to Knowledge Bases for Amazon Bedrock documentation. To get started, visit the Amazon Bedrock console or utilize the RetrieveAndGenerate API.
Read More for the details.

Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) for MySQL announces Amazon RDS Extended Support minor version 5.7.44-RDS.20240408. We recommend that you upgrade to this version to fix known security vulnerabilities and bugs in prior versions of MySQL. Learn more about upgrading your database instances, including minor and major version upgrades, in the Amazon RDS User Guide. Amazon RDS Extended Support provides you more time, up to three years, to upgrade to a new major version to help you meet your business requirements. During Extended Support, Amazon RDS will provide critical security and bug fixes for your MySQL and PostgreSQL databases on Aurora and RDS after the community ends support for a major version. You can run your MySQL databases on Amazon RDS with Extended Support for up to three years beyond a major version’s end of standard support date. Learn more about Extended Support in the Amazon RDS User Guide and the Pricing FAQs. Amazon RDS for MySQL makes it simple to set up, operate, and scale MySQL deployments in the cloud. See Amazon RDS for MySQL Pricing for pricing details and regional availability. Create or update a fully managed Amazon RDS database in the Amazon RDS Management Console.
Read More for the details.

Today, AWS has announced that Bottlerocket, the Linux-based operating system purpose-built for containers, now supports NVIDIA Fabric Manager, enabling users to harness the power of multi-GPU configurations for their AI and machine learning workloads. With this integration, Bottlerocket users can now seamlessly leverage their connected GPUs as a high-performance compute fabric, enabling efficient and low-latency communication between all the GPUs in each of their P4/P5 instances. The growing sophistication of deep learning models has led to an exponential increase in the computational resources required to train them within a reasonable timeframe. To address this increase in computational demands, customers running AI and machine learning workloads have turned to multi-GPU implementations, leveraging NVIDIA’s NVSwitch and NVLink technologies to create a unified memory fabric across connected GPUs. The Fabric Manager support in the Bottlerocket NVIDIA variants allows users to configure this fabric, enabling all GPUs to be used as a single, high-performance pool rather than individual units. This unlocks Bottlerocket users to run multi-GPU setups on P4/P5 instances, significantly accelerating the training of complex neural networks. To learn more about Fabric Manager support in the Bottlerocket NVIDIA variants, please visit the official Bottlerocket GitHub repo.
Read More for the details.

AWS HealthImaging now supports retrieval of DICOM Part 10 data, enabling customers to download instance-level binaries. The retrieve DICOM instance API is built in conformance to the DICOMweb WADO-RS standard for web-based medical imaging. With this feature launch, customers taking advantage of HealthImaging’s cloud-native interfaces can better interoperate with systems that utilize DICOM Part 10 binaries. You can retrieve a DICOM instance from a HealthImaging data store by specifying the Series, Study, and Instance UIDs associated with the resource. You can also provide an optional image set ID as a query parameter to specify the image set from which the instance resource should be retrieved. Customers can specify the Transfer Syntax, such as uncompressed (ELE) or compressed (High-throughput JPEG 2000). To learn more about how to retrieve DICOM P10 binaries, see the AWS HealthImaging Developer Guide. AWS HealthImaging is a HIPAA-eligible service that empowers healthcare providers and their software partners to store, analyze, and share medical images at petabyte scale. With AWS HealthImaging, you can run your medical imaging applications at scale from a single, authoritative copy of each medical image in the cloud, while reducing total cost of ownership. AWS HealthImaging is generally available in the following AWS Regions: US East (N. Virginia), US West (Oregon), Asia Pacific (Sydney), and Europe (Ireland). To learn more, visit AWS HealthImaging.
Read More for the details.

We are excited to announce that Knowledge Bases for Amazon Bedrock (KB) now lets you configure inference parameters to have greater control over personalizing the responses generated by a foundation model (FM). With this launch you can optionally set inference parameters to define parameters such randomness and length of the response generated by the foundation model. You can control how random or diverse the generated text is by adjusting a few settings, such as temperature and top-p. The temperature setting makes the model more or less likely to choose unusual or unexpected words. A lower value for temperature generates expected and more common word choices. The top-p setting limits how many word options the model considers. Reducing this number restricts the consideration to a smaller set of word choices makes the output more conventional. In addition to randomness and diversity, you can restrict the length of the foundation model output, through maxTokens, and stopsequences. You can use the maxTokens setting to specify the minimum or maximum number of tokens to return in the generated response. Finally, the stopsequences setting allows you to configure strings that serve as control for the model to stop generating further tokens. The inference parameters capability within Knowledge Bases is now available in Asia Pacific (Singapore), Asia Pacific (Sydney), Asia Pacific (Tokyo), Europe (Frankfurt), US East (N. Virginia), US West (Oregon) regions. To learn more, refer to Knowledge Bases for Amazon Bedrock documentation. To get started, visit the Amazon Bedrock console or utilize the RetrieveAndGenerate API.
Read More for the details.

Amazon Managed Streaming for Apache Kafka (Amazon MSK) now supports removing brokers from MSK provisioned clusters. Administrators can optimize costs of their Amazon MSK clusters by reducing broker count to meet the changing needs of their streaming workloads, while maintaining cluster performance, availability, and data durability. Customers use Amazon MSK as the core foundation to build a variety of real-time streaming applications and high-performance event driven architectures. As their business needs and traffic patterns change, they often adjust their cluster capacity to optimize their costs. Amazon MSK Provisioned provides flexibility for customers to change their provisioned clusters by adding brokers or changing the instance size and type. With broker removal, Amazon MSK Provisioned now offers an additional option to right-size cluster capacity. Customers can remove multiple brokers from their MSK provisioned clusters to meet the varying needs of their streaming workloads without any impact to client connectivity for reads and writes. By using broker removal capability, administrators can adjust cluster’s capacity, eliminating the need to migrate to another cluster to reduce broker count. Brokers can be removed from Amazon MSK provisioned clusters configured with M5 or M7g instance types. The feature is available in all AWS Regions where MSK Provisioned is supported. To learn more, visit our launch blog and the Amazon MSK Developer Guide.
Read More for the details.

Customers tell us they see great potential in using large language models (LLMs) with their data to improve customer experiences, automate internal processes, access and find information, and create new content —just to name a few of the emerging generative AI use cases. There are many ways to leverage your data, so in this blog, we’ll discuss some of the main approaches and applications, and what you need to know to get started.
Before we get started visualizing a generative AI application, we need to understand the ways in which LLMs and other foundation models can interact with your data.
Prompt engineering
The easiest way to facilitate interactions between a model and your data is to include the data in the instructions, or system prompt, sent to the model. In this approach, the model doesn’t need to be changed or adapted — which is very powerful and attractive, but also potentially limiting for some use cases. For example, whereas static information could be easily added to a system prompt and used to steer interactions, the same isn’t true for information that is frequently updated, such as sports scores or airline prices.
Retrieval augmented generation (RAG)
Retrieval augmented generation, or RAG, helps ensure model outputs are grounded on your data. Instead of relying on the model’s training knowledge, AI apps architected for RAG can search your data for information relevant to a query, then pass that information into the prompt. This is similar to prompt engineering, except that the system can find and retrieve new context from your data with each interaction.
The RAG approach supports fresh data that’s constantly updated, private data that you connect, large-scale and multimodal data, and more — and it’s supported by an increasingly robust ecosystem of products, from simple integrations with databases to embedding APIs and other components for bespoke systems.
Supervised fine-tuning (SFT)
If you want to give a model specific instructions for a well-defined task, you might consider SFT, also often referred to as Parameter Efficient Fine Tuning (PEFT). This can work well for tasks like classification, or creating structured outputs from free text.
To perform supervised fine tuning, you need to have the model learn from input-output pairs that you provide the model. For example, if you want to classify meeting transcripts into different categories (for example, “marketing,” “legal.” “customer-support”), then you’ll need to provide the supervised tuning process multiple transcripts along with the categories of the meetings. The tuning process will learn what you consider to be the right classification for your meetings.
Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF)
What if your goal is not well described into categories or isn’t easy to quantify? For example, suppose you want a model to have a certain tone (perhaps to have a brand voice, or to be formal in specific ways). Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback, or RLHF, is a technique that creates a model that is tuned to your specific needs, enhanced by a human’s preferences.
The algorithm looks like the following in a nutshell: You provide your data in the form of input prompts and output responses, but the output responses have to be in pairs: two plausible responses but one that you prefer over the other. For example, one might be correct but generic while the other is both correct and uses a language style that you want in your outputs.
Distillation
The clever technique of distillation combines two goals: creating a smaller model that is faster and quicker to process data, and making that model more specific to your tasks. It works by using a larger foundation model to “teach” a smaller model, and by focusing that teaching on your data and task. For example, imagine you want to double-check all your emails to make them more formal—and you want to do this with a smaller model. To achieve this, you give the input (the original text and the instruction “make this email more formal”) to the large model, and it gives you the output (the re-written email). Now, equipped with your inputs and the large model outputs, you can train a small specialized model to learn to reproduce this specific task. In addition to the foundation models input/output pairs, you can provide your own as well.
Which one to go for?
The first question to consider is: do you need the model to always give a citation of a source grounded in your data? If yes, you will need to use RAG. RAG also has the benefit that you can control who has access to which grounding data (based on who’s calling the model). That will help you combat hallucinations and enhance interpretability of the results.
If you don’t have those requirements, you’ll need to decide if prompt engineering is enough, or if you need to tune the model. If you have only a small amount of data, then prompt engineering may suffice — and with context windows continuing to grow, as evidenced by Gemini 1.5’s 1 million-token window, prompt engineering is becoming viable for large amounts of data as well..
If you choose tuning, then you’ll need to consider tuning options in accordance with how specific and difficult to quantify your desired model’s behavior is. In cases where your desired model produces an output that’s difficult to describe, human involvement is probably needed, so RLHF is the way to go. Otherwise, different tuning methods could be chosen considering how much personalization you need for your model, your budget, and how fast serving speed you require.
This decision tree is a simplified version of the reasoning we describe:
You may ask: why can’t I use more methods? For example: I want to fine-tune my model to have my brand voice and I also want it to use only my data to generate answers (RAG). That is also possible and often the best option! You can tune a model and then use it to perform another task. Or you can also tune an LLM and then perform in-context prompt engineering on it to make sure the model behaves as desired. To sum up, you can freely combine the aforementioned methods at your convenience.
Start simple. Not only that will speed you up, it will also give you a baseline from where to experiment and test what works best for your application.
You can try out all these capabilities on Google Cloud! Try Prompt Engineering, Vertex AI Agent Builder’s implementation of RAG, or if you would like to go for your own implementation of RAG, try our Embeddings or Multimodal Embeddings API to create them, and Vector Search to store them. Furthermore, experiment with Supervised Fine Tuning, Tuning with RLHF, and Distillation. And you can have a look at our code samples to help you.
Read More for the details.

ExpressRoute customers can now deploy a second gateway to the Gateway Subnet. This will enable a seamless migration to an Az-enabled Gateway SKU and upgrade your Public IP configurations.
Read More for the details.

Welcome to the first Cloud CISO Perspectives for May 2024. In this update, I’ll review my RSA Conference fireside chat with Mandiant CEO Kevin Mandia.
As with all Cloud CISO Perspectives, the contents of this newsletter are posted to the Google Cloud blog. If you’re reading this on the website and you’d like to receive the email version, you can subscribe here.
–Phil Venables, VP, TI Security & CISO, Google Cloud
By Phil Venables, VP, TI Security & CISO, Google Cloud
This year’s RSA Conference is just in our rearview mirror, and Google Cloud continued to make important announcements there. We unveiled Google Threat Intelligence and Google Security Operations, advanced our approach to AI and security, and demonstrated how our partners are enthusiastically embracing our security values.
Phil Venables, VP, TI Security & CISO, Google Cloud
Along with our announcements, we kicked off the conference with an on-stage conversation between Kevin Mandia and myself, and moderated by Jerry Archer, former CISO of Sallie Mae and now CSA federal liaison for quantum computing and artificial intelligence, as part of the Cloud Security Alliance. We had a wide-ranging discussion that covered the gamut of modern security challenges, including AI, nation-state attacks, government regulations, and of course, the important role that CISOs play in securing their organizations.
Since we covered so many topics, I thought it would be helpful to summarize our discussion from a high level.
AI: Hype versus reality, and the broader risks we face
We started our fireside chat by jumping straight into AI, which has the potential to revolutionize cybersecurity. We’re already seeing benefits in areas such as malware analysis, where as a demonstration of its capabilities, we were able to use AI to help us reverse engineer WannaCry and find its killswitch in a single pass — in 34 seconds.
We began by discussing concerns about how some security leaders and organizations are focusing on micro-risks such as model poisoning and prompt injection while neglecting broader issues.Those bigger issues can be thought of as three key pillars of AI risk: data management (which includes training, fine-tuning, parameters, and testing), AI software lifecycle management, and operational risk of deployment (including input and output guards, and circuit breakers.)Kevin clarified that AI will not replace all security jobs: There’s no single AI model that will work for everyone, and each organization will need to control their own models and biases.We’re now entering into the “data as code” era, where the importance of data management in AI will play a growing and crucial role in AI systems.
AI applications in security
Generative AI looks like it will have an impressive impact on cybersecurity. Gen AI models such as Google Cloud’s SecLM, which can help with tasks such as the aforementioned malware decoding, vulnerability analysis, and secure code generation, will need to be governed by a risk-management foundation such as our Secure AI Framework in order to maximize impact and mitigate risk.AI has the potential to improve mundane workflows, especially with incident write-ups and analysis.Mandiant now uses AI for threat intelligence, report generation, and investigation acceleration, while still emphasizing the need for human oversight and transparency in AI-driven decisions.Gen AI and traditional machine learning have the potential to create remarkable impacts on anomaly detection.
Why CISOs matter
As an industry, we are shifting to a risk-based approach to security. The ability of AI to assess and mitigate risks could help facilitate a move from maturity-based security programs to risk-based models. Combined with concerns over data security risks and operational risks, this could further evolve the role of CISO to a “chief digital risk officer.”CISOs can help drive the use of AI to advance institutional checks and balances, especially with risk and compliance. AI could be used to help with identity and access management, privileged reviews, and separation of duties.AI systems should be tested, just like any other system. AI can be used to evaluate the security and efficacy of other AI and it can act as an input and output guard. Still we need to use human red teams to ensure trust and safety, and to find edge cases.We can expect to see opportunities for CISOs to take on more responsibility in areas such as software security and AI governance, leading to increased empowerment and a more strategic role.
Defending against nation-state attacks, using regulations to achieve goals
Defenders need to use AI to advance their security goals if for no other reason than malicious actors are using AI to find vulnerabilities and launch zero-day attacks.Especially in light of the recent Cybersecurity Review Board report, industry collaboration can play a vital role in promoting higher standards for tech companies.This is where umbrella organizations such as the CSA can help: As an industry, we need clear and consistent standards for cloud providers and SaaS companies to drive security uplift and manage change.Not all security objectives are directly related to cybersecurity. We must be able to balance issues such as data sovereignty and localization, and ensure that they support security goals. To do so, we need clear delineation and appropriate controls for each objective.
If you missed us at RSAC, you can use our insider’s guide to revisit Google Cloud keynotes, panels, and presentations from the conference. To learn more, you can contact us at Ask Office of the CISO and come meet us at our security leader events.
Here are the latest updates, products, services, and resources from our security teams so far this month:
Advancing the art of AI-driven security with Google Cloud: AI has the power to revolutionize cybersecurity. Read our latest advancements and announcements from the RSA Conference here. Read more.Introducing Google Threat Intelligence: Actionable threat intelligence at Google scale: Google Threat Intelligence is a new offering that combines Mandiant, VirusTotal, and Google technologies and resources with Gemini to deliver unparalleled visibility into the global threat landscape. Read more.Introducing Google Security Operations: Intel-driven, AI-powered SecOps: This update to Google Security Operations is designed to reduce the DIY complexity of SecOps and enhance the productivity of your entire Security Operations Center. Read more.How to craft an Acceptable Use Policy for gen AI (and look smart doing it): Want to use AI in a safe, secure, dependable, and robust way? You should craft a “building code” for gen AI with your internal Acceptable Use Policy. Here’s how. Read more.Chrome Enterprise expands ecosystem to strengthen endpoint security and Zero Trust access: At RSAC, we announced a growing ecosystem of security providers who are working with us to extend Chrome Enterprise’s browser-based protections. Read more.The power of choice: Empowering your regulatory and compliance journey: At Google Cloud, we know you have diverse regulatory, compliance, and sovereignty needs, so at Next ‘24 we announced new ways to expand your power of choice. Read more.Securing the AI software supply chain: A new research publication: From the development lifecycles for traditional and AI software to the specific risks facing the AI supply chain, this new report explains our approach to securing our AI supply chain using provenance information and provides guidance for other organizations. Read more.Google is named a Visionary in the 2024 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for SIEM: We’re excited to share that Gartner has recognized Google as a Visionary in the 2024 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for SIEM, our first time participating. Read more.Automatically disabling leaked service account keys: What you need to know: Starting June 16, exposed service account keys that have been detected in services including public repos will be automatically disabled by default for new and existing customers. Read more.
Please visit the Google Cloud blog for more security stories published this month.
From assistant to analyst: The power of Gemini 1.5 Pro for malware analysis: This study investigates how Gemini 1.5 Pro can impact malware deconstruction and analysis, including reverse engineering WannaCry and finding its killswitch in 34 seconds. Read more.A practical guide to ransomware protection and containment strategies: Mandiant has updated its Ransomware Protection and Containment Strategies report, with expanded strategies that organizations can proactively take to identify gaps and harden their environments to prevent the downstream impact of a ransomware event. Read more.Uncharmed: Untangling Iran’s APT42 operations: Mandiant experts explore APT42, an Iranian state-sponsored cyber espionage actor who uses enhanced social engineering schemes to gain access to victim networks, including cloud environments. They target Western and Middle Eastern NGOs, media organizations, academia, legal services, and activists. Read more.
Looking back at the RSAC that just was: From the show floor to the keynote hall to the catered lunch, hosts Anton Chuvakin and Tim Peacock review this year’s conference, and what it bodes for getting real with gen AI, the future of SecOps, and maybe even the decline of XDR. Listen here.Defending against the dark side of gen AI: How are threat actors using gen AI right now, and how do we expect them to get better at it? Elie Bursztein, cybersecurity research lead, Google DeepMind, goes deep into the dark with Anton and Tim. Listen here.Getting real with gen AI: Redefining SecOps with practical AI applications: Security Operations Centers have been down the road of automation before with UEBA and SOAR. AI looks a lot like those but with more matrix math. Payal Chakravarty, director of product management, Google SecOps, discusses with Anton and Tim the promises and challenges of AI in the SOC. Listen here.Defender’s Advantage: Digging into M-Trends 2024: Jurgen Kutscher, vice president, Mandiant Consulting, joins host Luke McNamara to discuss the findings of the M-Trends 2024 report. Jurgen shares his perspective on the “By the Numbers” data, the theme of evasion of detection in this year’s report, and how Mandiant consultants have been using AI in purple and red teaming operations. Listen here.
To have our Cloud CISO Perspectives post delivered twice a month to your inbox, sign up for our newsletter. We’ll be back in two weeks with more security-related updates from Google Cloud.
Read More for the details.

Developing games is unique in that it requires a large variety of media assets such as 2D images, 3D models, audio, and video to come together in a development environment. However, in small game teams, such as those just getting started or “indie” teams, it’s unlikely that there are enough people to create such a wide variety and amount of assets. The lack of assets can create a bottleneck, throttling the entire game development team.
In this blog, we demonstrate how easy it is for gaming developers to deploy generative AI services on Google Cloud, showcase the available tooling of Model Garden on Vertex AI (including partner integrations like Hugging Face and Civitai), and highlight their potential for scaling game-asset creation.
Google Cloud offers a diverse range of generative AI models, accessible to users for various use cases. This solution focuses on how game development teams can harness the capabilities of Model Garden on Vertex AI, which incorporates partner integrations such as Hugging Face and Civitai.
Many artists run these models on their local machine, e.g., Stable Diffusion on a local instance of Automatic 1111. However, considering the cost of high-end GPUs, not all people have access to hardware required to do so. Therefore, running these models in the cloud is a way to access the compute needed while mitigating the need to invest in high-end hardware upfront.
Our primary objective is to explore how these tools can streamline and scale game-asset creation.
Assets are the visual and audio elements that make up a game’s world. They have a significant impact on the player’s experience, contributing to the creation of a realistic and immersive environment. There are many different types of game assets, including:
2D and 3D models
Textures
Animations
Sounds and music
Here’s a typical life journey of a typical 3D game asset, such as a character:
Concept art: Initial design of the asset
3D modeling: Creation of a three-dimensional model of the asset
Texturing: Adding color and detail to the model in alignment with the game’s style
Animation: Bringing movement to the asset (if applicable)
Sound effects: Adding audio elements to enhance the asset
Import to game engine: Integration of the asset into the game engine that powers the gameplay
Generative AI can streamline the asset-creation process by generating initial designs, 3D models, and high-quality textures tailored to the game’s style. In this way, game artists can quickly provide assets that unlock the rest of the game team in the short term, while allowing them to focus on long term goals like art direction and finalized assets.
Read on to learn how to accomplish the first step of game asset creation – generating concept art – on Google Cloud using Vertex AI and Model Garden with Stable Diffusion. We’ll cover how to access and download popular LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) adapters from Hugging Face or Civitai, and serve them alongside the stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0 model (from Model Garden) on Vertex AI for online prediction. The resulting concept art images will be stored in a Google Cloud Storage bucket for easy access and further refinement by artists.
1. Prerequisites:
Google Cloud Project: Select or create a project. When you first create an account, you get a $300 free credit towards your compute/storage costs.
Billing enabled: Verify that billing is enabled for your project.
APIs enabled: Enable both the Vertex AI and Compute Engine APIs.
2. Storage and authentication:
Cloud Storage Bucket: Create a bucket to store downloaded LORAs and experiment outputs.
Service Account: Create a service account with the following roles:
Vertex AI User
Storage Object Admin
We’ll use this service account with our Python notebook for model creation and storage management.
3. Colab Enterprise setup:
Runtime remplate: Create a runtime template in Colab Enterprise following the instructions at https://cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/docs/colab/create-runtime-template
Runtime instance: Create a runtime instance based on your Runtime template created above. Follow instructions at https://cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/docs/colab/create-runtime.
Upload notebooks: Download these three notebooks from git and upload them to the Colab Enterprise.
4. Running your notebooks:
Connecting notebooks: Once you’ve uploaded the notebooks, ensure they are connected to the runtime you created in step 3 above. This ensures your notebooks have access to the necessary resources for execution.
Cloud NAT: If your runtime environment requires internet access to download packages, you can create a Cloud NAT following these instructions.
This completes the infrastructure setup. You’re ready to run your Jupyter notebooks to deploy a LoRA model with stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0 on a Vertex AI prediction endpoint.
ExecutionUpon successful execution of all the above steps, you should see three Jupyter notebook files in Colab Enterprise as follows:
1. Create_mg_pytorch_sdxl_lora.ipynb
This notebook contains steps to download popular LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) adapters from either huggingface.co or civitai.com. It then serves the adapter alongside the stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0 model on Vertex AI for online prediction.
In this notebook, set the following variables to begin:
HUGGINGFACE_MODE: If enabled, the LoRA will be downloaded from Hugging Face. Otherwise, it will be downloaded from Civitai.
Upon successful execution, this notebook will print “Model ID” and “Endpoint ID.” Save these values for use in the following notebooks.
If HUGGINGFACE_MODE is unchecked or disabled, ensure you update the Civitai variables within the notebook.
2. GenerateGameAssets.ipynb
This notebook contains code to convert text to images. Set the following variables to begin:
ENDPOINT_ID: Obtained from successful execution of “1.Create_mg_pytorch_sdxl_lora.ipynb”.
Upon successful execution, you should see the following results:
Concept art images will be uploaded to your configured GCS storage bucket.
Images will be displayed for reference.
3. CleanupCloudResources.ipynb
Execute this notebook to clean up resources, including the endpoint and model.
Before executing, set the following variables:
MODEL_ID and ENDPOINT_ID: Obtained from successful execution of “1.Create_mg_pytorch_sdxl_lora.ipynb”.
Congratulations! You’ve successfully deployed the stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0 model from Model Garden on Vertex AI, generated concept art for your games, and responsibly deleted models and endpoints to manage costs.
Integrating Stable Diffusion-generated images into a game requires careful planning:
Legal rights: Ensure you have the necessary permissions to use generated images. Always consult a legal professional if you have any questions about image usage rights.
Customization: Edit and refine the images to match your game’s style and technical needs.
Optimization: Optimize images for in-game performance and smooth integration into your game engine.
Testing: Thoroughly test for quality and performance after incorporating the assets.
Ethics and compliance: Prioritize ethical considerations and legal compliance throughout the entire process.
Documentation and feedback: Maintain detailed records, backups, and be responsive to player feedback after your game’s release.
Explore AI models in Model Garden https://cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/docs/start/explore-models
Your guide to generative AI support in Vertex AI https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/ai-machine-learning/vertex-ai-model-garden-and-generative-ai-studio
Read More for the details.

In today’s cloud-driven world, optimization isn’t an option – it’s your competitive advantage. When you streamline cloud costs, you free up resources that you can reinvest into innovation, research and development, accelerating new product development, or fueling market expansion.
But let’s get real: optimizing cloud environments at scale can be overwhelming. Managing large datasets, navigating usage-based pricing, and coordinating across multiple teams can feel like impossible challenges. That’s where FinOps hub comes in!
FinOps hub enables you to supercharge your FinOps practices and optimize costs with intelligent insights and actionable recommendations. Rightsize resources, reduce waste, and rate optimization with committed use discounts (CUDs), so you can invest those savings directly into innovation. FinOps hub is now generally available.
FinOps hub – your command center for FinOps optimization
FinOps hub’s comprehensive cloud optimization solution is designed to solve the biggest challenges faced by FinOps teams. It blends rate and usage strategies with personalized prescriptions tailored to your business needs. Plus, you can track your accomplishments with an easy-to-use realized savings ledger.
These are the key features of FinOps hub:
With FinOps hub, you can easily comprehend your cost-saving performance indicators. These indicators include both realized savings and potential savings achievable through active recommendations. Starting today, you can identify the projects that have the highest savings potential. This enables you to prioritize your optimization efforts and focus on the areas that will yield the greatest financial benefits.
NEW – Widget showing potential savings by project
Leverage our advanced recommendation algorithms and analytics to identify opportunities for rightsizing workloads, reducing waste, and maximizing committed-based discounts, helping to ensure efficient resource utilization and achieving significant cost savings.
Whether you’re a FinOps expert or just getting started, the Top Recommendations widget simplifies your journey. It highlights the most impactful and easy-to-implement cost-saving opportunities for your business.
Top recommendations widget in FinOps hub
FinOps hub supports recommendations for multiple products across multiple recommender engines. It can help you optimize costs for key services across Google Cloud, including Compute Engine, Google Kubernetes Engine, Cloud SQL, Cloud Run, and more (see more details here).
Understand and optimize your FinOps practices through in-depth analysis of your Google Cloud usage patterns, enabling continuous improvement and better financial accountability across your teams. Peer benchmarks (with an opt-out option) provide you with more context into how you are performing with FinOps practices, as well as the overall rate optimizations through committed use discounts (CUDs).
Google Cloud FinOps score
The CUD optimization widget offers three key performance indicators (KPIs) to help you get the biggest benefits from your commitments. The first KPI, “Last month’s realized CUD savings”, helps you measure how much money you’re saving with CUDs across all eligible Google Cloud services used by your billing account. “Optimization rate for Your billing account” analyzes your total product usage over the past month to determine if you have opportunities to optimize your spending further through CUDs. Finally, the peer benchmark helps you get perspective into your overall performance.
Google Cloud CUD Optimization Rate
Getting started with FinOps hub is quick and easy. Its intuitive interface and powerful features are designed to streamline your optimization efforts and deliver measurable results from day one.
You will need the Billing Account Administrator or the Billing Account Viewer role to access the FinOps hub and view available recommendations, the FinOps Score and CUDs optimization metrics, and the metrics that inform cost optimization across projects associated with your billing account.
Visit FinOps hub to find your cost optimization opportunities today.
Read More for the details.

Dataflow, Google Cloud’s fully managed streaming analytics service, has a proud tradition of getting the job done (pun intended) with completeness and with precision. Practically speaking, that means leaving no shard behind and doing things exactly once. Today, we are excited to announce three new features: straggler detection, hot key detection, and slow worker auto-mitigation.
Stragglers are tasks that take significantly longer to complete than the average task of the same type. This can happen for a variety of reasons, such as hardware differences, network conditions, or uneven data distribution. Stragglers can cause a number of problems for data processing pipelines, including increased latency, reduced throughput, and increased costs.
Dataflow helps users deal with stragglers in three ways:
In-context tooling for detailed diagnosis: Dataflow provides a variety of observability tools to help users identify and diagnose stragglers.
Root-cause analysis: Dataflow analyzes stragglers to identify the root cause of the problem. This information can be used to prevent future stragglers from occurring.
Auto-mitigation: Wherever possible, Dataflow automatically prevents and mitigate stragglers with proactive load balancing and fixing unhealthy nodes.
This approach helps users minimize the impact of stragglers on their pipelines.
The first strategy for dealing with stragglers in Dataflow is in-context observability. We help users identify if there are stragglers and which node and worker they are occurring on. This allows users to quickly drill deeper into the pipeline to diagnose and mitigate the straggler.
Before we go further, it is helpful to go over some key terms:
Step: Reads, writes, and transformations defined by user code
Fusion: The process of Dataflow fusing multiple steps or transforms to optimize a pipeline
Stage: The unit of fused steps in Dataflow pipelines
Dataflow’s new straggler detection feature helps customers identify when pipelines contain stragglers.
Batch detection
A work item is considered a straggler if ALL THREE conditions are satisfied:
It takes an order of magnitude longer to complete than other work items in the same stage.
It reduces parallelism within the stage.
It blocks new work from starting.
Streaming detection
A work item is considered a straggler if ALL THREE conditions are satisfied:
The stage the work item is running in has to have a watermark lag of > 10 min.
The work item has been processing for > 5 min.
The work item has been processing for 1.5 times longer than the average work item in that stage.
Once detected, stragglers are surfaced in the UI under the Execution Details tab (batch/streaming). You’ll be able to filter your logs to the user worker on which the straggler was detected during the incident’s time-frame (batch/streaming).
Once a straggler is identified, Dataflow attempts to determine the cause where possible. There are a number of factors that can create stragglers, so pinpointing the underlying root cause saves debugging time and lets you focus on mitigating the issue.
A hot key is a key that represents significantly more elements than other keys in the same PCollection (i.e., input data that is skewed). Hot keys can stifle Dataflow’s ability to perform work in parallel as they introduce long chains of sequential work into the parallel job.
Dataflow automatically detects when a hot key occurs. Additionally, when jobs are run with the `hotKeyLoggingEnabled` pipeline option enabled, Dataflow logs the detected key to help with debugging.
Hot keys typically cannot be fully remediated with performance levers such as horizontally or vertically scaling your workers. Instead, solving hot keys often requires evaluating your pipeline’s steps and narrowing in on where keys may become disproportionately distributed.
An example of a remediation strategy is the use of a shuffle. Given a dataset that has uneven distribution around a key, a user can add an extra sharding key. This further partitions the data into smaller chunks, thereby increasing parallelism.
Your best defense against stragglers in Dataflow is auto-mitigation. This proactively avoids straggler impact to pipelines, with no intervention on your part required. As a fully managed service, Dataflow aims to provide “zero-knobs” solutions wherever possible so you can focus on your business logic without having to worry about managing the underlying infrastructure.
Dataflow’s dynamic work rebalancing feature can help to prevent stragglers by identifying them early and redistributing their work to other workers. It works by monitoring the progress of each worker in the pipeline and redistributing work to workers that are finishing faster. This helps to ensure that all of the workers are working at approximately the same rate.
Dataflow auto-mitigates stragglers caused by slow workers. Many factors can cause worker slowness, such as CPU starvation, thrashing, problematic machine architecture, and stuck worker processes. On a slow worker, work items will be processed much more slowly than they should be and eventually result in a straggler.
When a slow worker is detected, the auto-mitigation feature simulates a host maintenance event to trigger the worker’s host maintenance policy for a live migration, restart, or stop. If a live migration occurs, the processed work on the slow worker will be transitioned seamlessly to a new worker without losing progress or any in-flight data.
If a slow worker is detected and successfully auto-mitigated, the following message displays in the Dataflow job-message logs: Slow worker … detected and automatically remediated …. Because slow workers are not stragglers but a cause of stragglers, once it’s remediated, you don’t need to take further action.
To learn more about troubleshooting stragglers in Dataflow, review these guides:
https://cloud.google.com/dataflow/docs/guides/troubleshoot-batch-stragglers
https://cloud.google.com/dataflow/docs/guides/troubleshoot-streaming-stragglers
We thank the Google Cloud team members who co-authored the blog: Claire McCarthy, Software Engineer, Matthew Li, Software Engineer, Ning Kang, Software Engineer, Sam Rohde, Software Engineer.
Read More for the details.

Amazon WorkSpaces Core now offers new bundles powered by Windows Server 2019 and Windows Server 2022. With these bundles, customers and partners can take advantage of the latest license included Windows Server instances. This new feature will allow customers to minimize getting started time by providing staged images. In addition, this feature enables customers and partners to run multi-session VDI workloads on WorkSpaces Core desktops. You can get started using the managed Windows Server 2019 and Windows Server 2022 WorkSpaces Core bundle or create your own custom bundle and image tailored to your requirements. For more information on Amazon WorkSpaces Core’s new Windows Server Bundles, visit Amazon WorkSpaces Core FAQs. The new WorkSpaces Core Windows Server 2019 and Windows Server 2022 support is available in all AWS Regions where Amazon WorkSpaces Core is available. For pricing information, visits Amazon WorkSpaces Core pricing page.
Read More for the details.

Amazon DocumentDB zero-ETL integration with Amazon OpenSearch Service provides customers advanced search capabilities, such as fuzzy search, cross-collection search and multilingual search, on their Amazon DocumentDB documents using the OpenSearch API. With a few clicks in the AWS Console, customers can now seamlessly synchronize their data from Amazon DocumentDB to Amazon OpenSearch Service, eliminating the need to write any custom code to extract, transform, and load the data. This integration extends the existing text search and vector search capabilities in Amazon DocumentDB, providing customers greater flexibility for searching their JSON-based documents. This zero-ETL integration uses Amazon OpenSearch Ingestion to synchronize the data from Amazon DocumentDB collections to Amazon OpenSearch Service. Amazon OpenSearch Ingestion is able to automatically understand the format of the data in Amazon DocumentDB collections and maps the data to your index mapping templates in Amazon OpenSearch Service to yield the most performant search results. Customers can synchronize data from multiple Amazon DocumentDB collections via multiple pipelines into one Amazon OpenSearch managed cluster or serverless collection to offer holistic insights across several applications. Amazon DocumentDB zero-ETL integration with Amazon OpenSearch Service is now available in the following 13 regions : US East (Ohio), US East (N. Virginia), US West (Oregon), Europe (Ireland), Europe (London), Europe (Frankfurt), Asia Pacific (Tokyo), Asia Pacific (Sydney), and Asia Pacific (Singapore), Asia Pacific (Mumbai), Asia Pacific (Seoul), and Canada (Central). To learn more and get started with this zero-ETL integration, visit the developer guides for Amazon DocumentDB and Amazon OpenSearch Service and the launch blog.
Read More for the details.

Amazon Managed Service for Prometheus now supports inline editing of rules and alert manager configuration directly from the AWS console. Amazon Managed Service for Prometheus is a fully managed Prometheus-compatible monitoring service that makes it easy to monitor and alarm on operational metrics at scale. Prometheus is a popular Cloud Native Computing Foundation open-source project for monitoring and alerting on metrics from compute environments such as Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service. Previously, customers could define alerting and recording rules, or alert manager definition, by importing respective configuration defined in a YAML file, via the AWS console. Now, they can import, preview, and edit existing rules or alert manager configurations from YAML files or create them directly from the AWS console. The inline editing experience allows customers to preview their rules and alert manager configuration prior to setting them. This feature is now available in all regions where Amazon Managed Service for Prometheus is generally available. To learn more about Amazon Managed Service for Prometheus, visit the product page and pricing page.
Read More for the details.